-
Effect of casein phosphopeptide-amorphous calcium phosphate on fluoride release and micro-shear bond strength of resin-modified glass ionomer cement in caries-affected dentin
-
Jamila Nuwayji Agob, Neven Saad Aref, Essam El Saeid Al-Wakeel
-
Restor Dent Endod 2018;43(4):e45. Published online October 30, 2018
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2018.43.e45
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
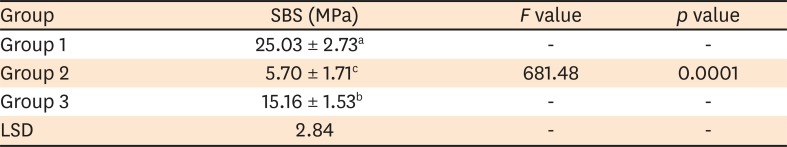
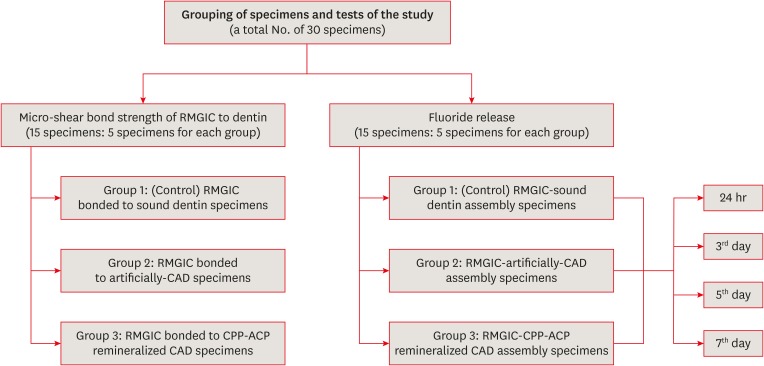
This study was conducted to evaluate fluoride release and the micro-shear bond strength of resin-modified glass ionomer cement (RMGIC) in casein phosphopeptide-amorphous calcium phosphate (CPP-ACP)-remineralized caries-affected dentin (CAD). Materials and MethodsExposed dentin surfaces of 30 human third molar teeth were divided into 2 equal groups for evaluating fluoride release and the micro-shear bond strength of RMGIC to CAD. Each group was subdivided into 3 equal subgroups: 1) control (sound dentin); 2) artificially demineralized dentin (CAD); 3) CPP-ACP remineralized dentin (remineralized CAD). To measure fluoride release, 15 disc-shaped specimens of RMGIC (4 mm in diameter and 2 mm in thickness) were bonded on one flat surface of the dentin discs of each group. Fluoride release was tested using ion chromatography at different intervals; 24 hours, 3, 5, 7 days. RMGIC micro-cylinders were built on the flat dentin surface of the 15 discs, which were prepared according to the assigned group. Micro-shear bond strength was measured after 24 hours water storage. Data were analyzed using 1- and 2-way analysis of variance and the post hoc least significant difference test (α = 0.05). ResultsFluoride detected in solutions (at all intervals) and the micro-shear bond strength of RMGIC bonded to CPP-ACP-remineralized dentin were significantly higher than those bonded to artificial CAD (p < 0.05). ConclusionsDemineralized CAD consumes more fluoride released from RMGIC into the solution for remineralization than CPP-ACP mineralized dentin does. CPP-ACP increases the micro-shear bond strength of RMGIC to CAD.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Synergistic effect of nanosilver fluoride with L-arginine on remineralization of early carious lesions
Ahmad S. Albahoth, Mi-Jeong Jeon, Jeong-Won Park
Scientific Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of the bond strength of glass ionomer cement modified with fluoride-loaded chitosan nanoparticles to caries-affected dentin
Hanife Altınışık, Merve Nezir, Hülya Erten Can, Necibe Başaran Mutlu Ağardan, Aysel Berkkan
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Non-collagenous protein analog-induced biomimetic mineralization strategy to restore the dentin interface
Ruhua Chen, Yimeng Xie, Liang Ma, Bing Li, Wei Yao
Biomedical Physics & Engineering Express.2024; 10(6): 062004. CrossRef - A Critical Review on the Factors Affecting the Bond Strength of Direct Restorative Material Alternatives to Amalgam
Zeynep Batu Eken, Nicoleta Ilie
Materials.2024; 17(19): 4853. CrossRef - ÇOCUK DİŞ HEKİMLİĞİNDE GÜMÜŞ DİAMİN FLORÜR KULLANIMI
Zeynep UÇAR, Bahar Melis AKYILDIZ
Selcuk Dental Journal.2022; 9(2): 652. CrossRef - Microshear Bond Strength of Nanoparticle-Incorporated Conventional and Resin-Modified Glass Ionomer to Caries-Affected Dentin
Zahra Fattah, Zahra Jowkar, Safoora Rezaeian, Lucas da Fonseca Roberti Garcia
International Journal of Dentistry.2021; 2021: 1. CrossRef
-
1,988
View
-
12
Download
-
6
Crossref
|