-
Effect of different storage media on elemental analysis and microhardness of cervical cavity margins restored with a bioactive material
-
Hoda Saleh Ismail, Brian Ray Morrow, Ashraf Ibrahim Ali, Rabab Elsayed Elaraby Mehesen, Salah Hasab Mahmoud, Franklin Garcia-Godoy
-
Restor Dent Endod 2024;49(1):e6. Published online January 17, 2024
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2024.49.e6
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
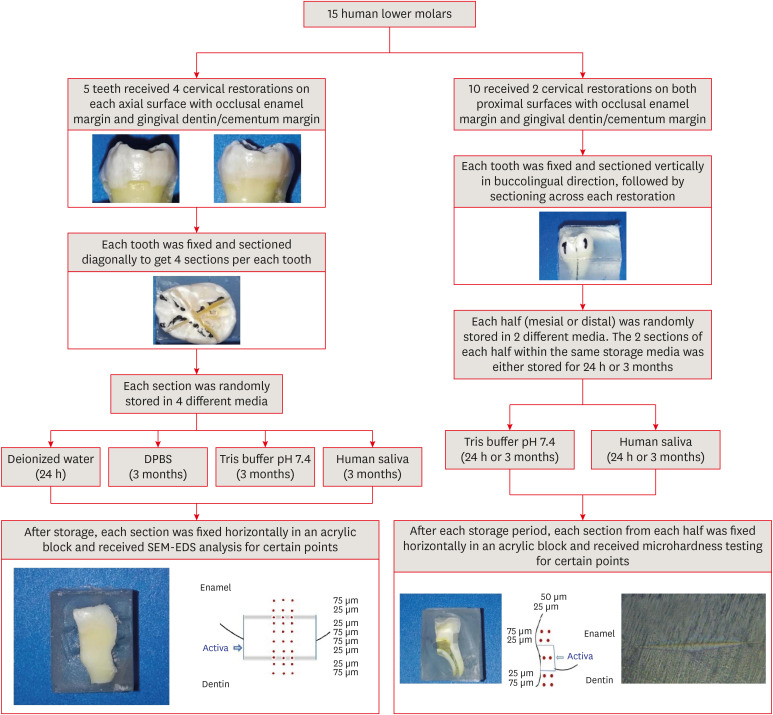
This study aimed to investigate the elemental analysis and microhardness of a bioactive material (Activa) and marginal tooth structure after storage in different media. Materials and MethodsFifteen teeth received cervical restorations with occlusal enamel and gingival dentin margins using the tested material bonded with a universal adhesive, 5 of them on the 4 axial surfaces and the other 10 on only the 2 proximal surfaces. The first 5 teeth were sectioned into 4 restorations each, then stored in 4 different media; deionized water, Dulbecco's phosphate buffered saline (DPBS), Tris buffer, and saliva. The storage period for deionized water was 24 hours while it was 3 months for the other media. Each part was analyzed by scanning electron microscopy-energy dispersive spectroscopy (SEM-EDS) analysis for different substrates/distances and the wt% of calcium, phosphorus, silica, and fluoride were calculated. The other 10 teeth were sectioned across the restoration, stored in either Tris buffer or saliva for 24 hours or 3 months, and were evaluated for microhardness of different substrates/areas. Data were analyzed using analysis of variance and Tukey’s post hoc test. ResultsEnamel and dentin interfaces in the DPBS group exhibited a significant increase in calcium and phosphorus wt%. Both silica and fluoride significantly increased in tooth structure up to a distance of 75 μm in the 3-month-media groups than the immediate group. Storage media did not affect the microhardness values. ConclusionsSEM-EDS analysis suggests an ion movement between Activa and tooth structure through a universal adhesive while stored in DPBS.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Influence of curing mode and aging on the bonding performance of universal adhesives in coronal and root dentin
Hoda Saleh Ismail, Ashraf Ibrahim Ali, Mohamed Elshirbeny Elawsya
BMC Oral Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef
-
304
View
-
32
Download
-
1
Web of Science
-
1
Crossref
|