-
Bioactivity of endodontic biomaterials on dental pulp stem cells through dentin
-
Bahar Javid, Narges Panahandeh, Hassan Torabzadeh, Hamid Nazarian, Ardavan Parhizkar, Saeed Asgary
-
Restor Dent Endod 2020;45(1):e3. Published online November 4, 2019
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2020.45.e3
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
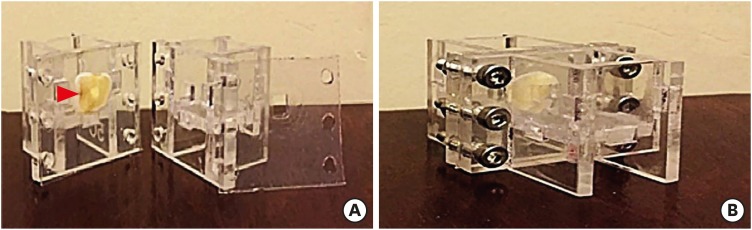
This study investigated the indirect effect of calcium-enriched mixture (CEM) cement and mineral trioxide aggregate (MTA), as 2 calcium silicate-based hydraulic cements, on human dental pulp stem cells (hDPSCs) through different dentin thicknesses. Materials and MethodsTwo-chamber setups were designed to simulate indirect pulp capping (IPC). Human molars were sectioned to obtain 0.1-, 0.3-, and 0.5-mm-thick dentin discs, which were placed between the 2 chambers to simulate an IPC procedure. Then, MTA and CEM were applied on one side of the discs, while hDPSCs were cultured on the other side. After 2 weeks of incubation, the cells were removed, and cell proliferation, morphology, and attachment to the discs were evaluated under scanning electron microscopy (SEM). Energy-dispersive X-ray (EDXA) spectroscopy was performed for elemental analysis. Alkaline phosphatase (ALP) activity was assessed quantitatively. The data were analyzed using the Kruskal-Wallis and Mann-Whitney tests. ResultsSEM micrographs revealed elongated cells, collagen fibers, and calcified nucleations in all samples. EDXA verified that the calcified nucleations consisted of calcium phosphate. The largest calcifications were seen in the 0.1-mm-thick dentin subgroups. There was no significant difference in ALP activity across the CEM subgroups; however, ALP activity was significantly lower in the 0.1-mm-thick dentin subgroup than in the other MTA subgroups (p < 0.05). ConclusionsThe employed capping biomaterials exerted biological activity on hDPSCs, as shown by cell proliferation, morphology, and attachment and calcific precipitations, through 0.1- to 0.5-mm-thick layers of dentin. In IPC, the bioactivity of these endodontic biomaterials is probably beneficial.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Dental pulp capping materials: modulators of stem cell behavior and regenerative potential
Ali Cheayto, Sara Ayoub, Sarah Ayad Al-Tameemi, Mohammad Fayyad-Kazan
Biomedical Physics & Engineering Express.2025; 11(6): 062004. CrossRef - Effect of pulp capping materials on odontogenic differentiation of human dental pulp stem cells: An in vitro study
Mahmoud M. Bakr, Mohamed Shamel, Shereen N. Raafat, Robert M. Love, Mahmoud M. Al‐Ankily
Clinical and Experimental Dental Research.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of Growth Factors on the Differentiation of Dental Stem Cells: A
Systematic Review and Meta-analysis (Part I)
Sayna Shamszadeh, Armin Shirvani, Hassan Torabzadeh, Saeed Asgary
Current Stem Cell Research & Therapy.2024; 19(4): 523. CrossRef - The Role of Growth Factor Delivery Systems on Cellular Activities of Dental
Stem Cells: A Systematic Review (Part II)
Sayna Shamszadeh, Armin Shirvani, Saeed Asgary
Current Stem Cell Research & Therapy.2024; 19(4): 587. CrossRef - Comprehensive review of composition, properties, clinical applications, and future perspectives of calcium-enriched mixture (CEM) cement: a systematic analysis
Saeed Asgary, Mahtab Aram, Mahta Fazlyab
BioMedical Engineering OnLine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of dental pulp stem cells behavior after odontogenic differentiation induction by three different bioactive materials on two different scaffolds
Basma Ahmed, Mai H. Ragab, Rania A. Galhom, Hayam Y. Hassan
BMC Oral Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Characterization of Dental Pulp Stem Cell Responses to Functional Biomaterials Including Mineralized Trioxide Aggregates
Sejin Bae, Bueonguk Kang, Hyungbin Lee, Harrison Luu, Eric Mullins, Karl Kingsley
Journal of Functional Biomaterials.2021; 12(1): 15. CrossRef - Incorporation of amoxicillin-loaded microspheres in mineral trioxide aggregate cement: an in vitro study
Fábio Rocha Bohns, Vicente Castelo Branco Leitune, Isadora Martini Garcia, Bruna Genari, Nélio Bairros Dornelles, Silvia Stanisçuaski Guterres, Fabrício Aulo Ogliari, Mary Anne Sampaio de Melo, Fabrício Mezzomo Collares
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2020;[Epub] CrossRef
-
1,480
View
-
12
Download
-
8
Crossref
|