-
In vitro evaluation of octenidine as an antimicrobial agent against Staphylococcus epidermidis in disinfecting the root canal system
-
Jia Da Chum, Darryl Jun Zhi Lim, Sultan Omer Sheriff, Shaju Jacob Pulikkotil, Anand Suresh, Fabian Davamani
-
Restor Dent Endod 2019;44(1):e8. Published online February 8, 2019
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2019.44.e8
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
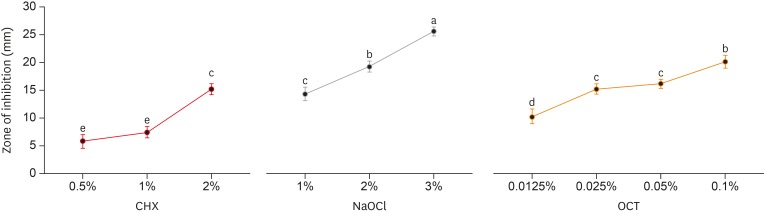
Irrigants are imperative in endodontic therapy for the elimination of pathogens from the infected root canal. The present study compared the antimicrobial efficacy of octenidine dihydrochloride (OCT) with chlorhexidine (CHX) and sodium hypochlorite (NaOCl) against Staphylococcus epidermidis (S. epidermidis) for root canal disinfection. Materials and MethodsThe minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) was obtained using serial dilution method. The agar diffusion method was then used to determine the zones of inhibition for each irrigant. Lastly, forty 6-mm dentin blocks were prepared from human mandibular premolars and inoculated with S. epidermidis. Samples were randomly divided into 4 groups of 10 blocks and irrigated for 3 minutes with saline (control), 2% CHX, 3% NaOCl, or 0.1% OCT. Dentin samples were then collected immediately for microbial analysis, including an analysis of colony-forming units (CFUs). ResultsThe MICs of each tested irrigant were 0.05% for CHX, 0.25% for NaOCl, and 0.0125% for OCT. All tested irrigants showed concentration-dependent increase in zones of inhibition, and 3% NaOCl showed the largest zone of inhibition amongst all tested irrigants (p < 0.05). There were no significant differences among the CFU measurements of 2% CHX, 3% NaOCl, and 0.1% OCT showing complete elimination of S. epidermidis in all samples. ConclusionsThis study showed that OCT was comparable to or even more effective than CHX and NaOCl, demonstrating antimicrobial activity at low concentrations against S. epidermidis.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - WITHDRAWN: Substantivity of different antiseptic oral gels. An In vitro study
Nirit Tagger Green, Roni Kolerman, Carlos Nemcovsky, Shlomo Matalon, Dan Gaukhman, Liat Chaushu
Heliyon.2025; : e42654. CrossRef - Evaluation of postoperative pain in endodontic retreatment with apical periodontitis using ozonated 2% chlorhexidine and 0.1% octenidine application: A randomized clinical trial
Nidhi Sinha, Geeta Asthana, Girish Parmar, Akshayraj Langaliya, Jinali Shah, Bijay Singh
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2024; 27(6): 654. CrossRef - Research on NiTi instruments combined with ultrasonic irrigation and multiantibiotic paste in root canal therapy of periapical inflammation in deciduous teeth
Zongxia Zhu, Guangli Fu
Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of antimicrobial efficacy of 0.1% octenidine dihydrochloride, superoxidized solution, ozonated water, 0.1% silver nanoparticle solution, and Q mix™ 2 in 1 in root canals infected with Enterococcus faecalis
Mahenaz Salam Inamdar, Dayanand G. Chole, Shrinivas S. Bakle, Preeti B. Vaprani, Neha P. Gandhi, Nikhil R. Hatte
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2024; 27(10): 1059. CrossRef - Causal relationship, shared genes between rheumatoid arthritis and pulp and periapical disease: evidence from GWAS and transcriptome data
Huili Wu, Lijuan Wang, Chenjie Qiu
Frontiers in Immunology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The effect of octenidine dihydrochloride on the antibacterial activity of a formulated resin composite: an in vitro study
Mahitab Mansour, Tarek Salah, Haidy N. Salem
Bulletin of the National Research Centre.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Association between pulp and periapical disease with type 2 diabetes: A bidirectional Mendelian randomization
Yuqiang Wang, Jiakang Zhu, Ying Tang, Cui Huang
International Endodontic Journal.2024; 57(5): 566. CrossRef - New Insights Regarding the Use of Relevant Synthetic Compounds in Dentistry
Stefania-Irina Dumitrel, Anamaria Matichescu, Stefania Dinu, Roxana Buzatu, Ramona Popovici, Dorin Dinu, Dana Bratu
Molecules.2024; 29(16): 3802. CrossRef - Formulation and Characterization of a Novel Palm-Oil-Based α-Mangostin Nano-Emulsion (PO-AMNE) as an Antimicrobial Endodontic Irrigant: An In Vitro Study
Omer Sheriff Sultan, Haresh Kumar A/L Kantilal, Khoo Suan Phaik, Hira Choudhury, Fabian Davamani
Processes.2023; 11(3): 798. CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of Antimicrobial Efficacy of Herbal Formulations of Septilin and Triphala with Conventional 2% Chlorhexidine on Root Canal and Oral Commensal Bacteria using Kirby Bauer Method
Shadab Ahmed, Kamil Shahnawaz, Tapan Kumar Mandal, Mamnoon Ghafir, Shiva Shankar Gummaluri, Gaurav Vishal
Contemporary Clinical Dentistry.2022; 13(4): 383. CrossRef - A comparative assessment of pomegranate extract, sodium hypochlorite, chlorhexidine, Myrrh (Commiphora molmol), tulsi extract against Enterococcus faecalis, Fusobacterium nucleatum and Staphylococci epidermidis
Mallwika Sisodiya, Shadab Ahmed, Ranjan Sengupta, Priyanka, Ankit Kumar Saha, Gourav Verma
Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Pathology.2021; 25(2): 369. CrossRef - Effects of Octenidine on the Formation and Disruption of Dental Biofilms: An Exploratory In Situ Study in Healthy Subjects
B. Reda, J. Dudek, M. Martínez-Hernández, M. Hannig
Journal of Dental Research.2021; 100(9): 950. CrossRef - Does Cavity Disinfectant Affect Sealing Ability of Universal Self-etch Adhesive?
S Lata, Prasanti Kumari Pradhan, Gaurav Patri, Subhasmita Bhol, Kanhu C Sahoo, Khushboo Ghosh
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2021; 22(3): 273. CrossRef - Effect of duration and dilution on antimicrobial efficacy of octenidine hydrochloride as an intracanal medicament with chitosan carrier against Enterococcus faecalis – A modified direct contact test
VinayaSusan Varghese, Nirmal Kurian
Journal of Conservative Dentistry.2020; 23(5): 463. CrossRef
-
258
View
-
5
Download
-
14
Crossref
-
Root canal irrigants influence the hydrophobicity and adherence of Staphylococcus epidermidis to root canal dentin: an in vitro study
-
Venkateshbabu Nagendrababu, Omer Sheriff Sultan, Sreedharan Kannathasan, Amir Shahreza Patel, Ebenezer Chitra, Prasanna Neelakantan, Fabian Davamani
-
Restor Dent Endod 2018;43(1):e1. Published online December 7, 2017
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2018.43.e1
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
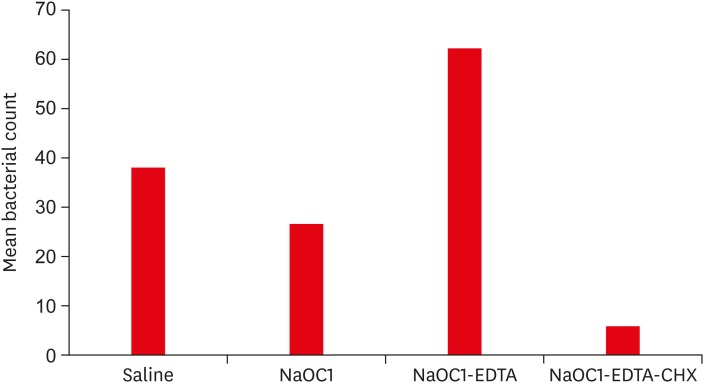
To determine the effect of root canal irrigants on the hydrophobicity and adherence of Staphylococcus epidermidis (S. epidermidis) to root canal dentin in vitro. Materials and MethodsRoot dentin blocks (n = 60) were randomly divided into 4 groups based on the irrigation regimen: group 1, saline; group 2, 5.25% sodium hypochlorite (NaOCl); group 3, 5.25% NaOCl followed by 17% ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA); group 4, same as group 3 followed by 2% chlorhexidine (CHX). The hydrophobicity of S. epidermidis to root dentin was calculated by cell surface hydrophobicity while the adherence was observed by fluorescence microscopy, and bacteria were quantified using ImageJ software (National Institutes of Health). Statistical analysis of the data was done using Kruskal-Wallis test and Mann-Whitney U test (p = 0.05). ResultsThe hydrophobicity and adherence of S. epidermidis to dentin were significantly increased after irrigating with group 3 (NaOCl-EDTA) (p < 0.05), whereas in group 4 (NaOCl-EDTA-CHX) both hydrophobicity and adherence were significantly reduced (p < 0.05). ConclusionsThe adherence of S. epidermidis to dentin was influenced differently by root canal irrigants. Final irrigation with CHX reduces the bacterial adherence and may impact biofilm formation.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Quaternary ammonium silane (k21) based intracanal medicament triggers biofilm destruction
Esther Sook Kuan Kok, Xian Jin Lim, Soo Xiong Chew, Shu Fen Ong, Lok Yin See, Siao Hua Lim, Ling Ang Wong, Fabian Davamani, Venkateshbabu Nagendrababu, Amr Fawzy, Umer Daood
BMC Oral Health.2021;[Epub] CrossRef
-
201
View
-
1
Download
-
1
Crossref
|