-
Comparative evaluation of Emblica officinalis as an etchant and an MMP inhibitor with orthophosphoric acid and chlorhexidine on the microshear bond strength of composite resin: an ex vivo study
-
Divya Sangeetha Rajkumar, Annapoorna Ballagere Mariswamy
-
Restor Dent Endod 2021;46(3):e36. Published online June 8, 2021
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2021.46.e36
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
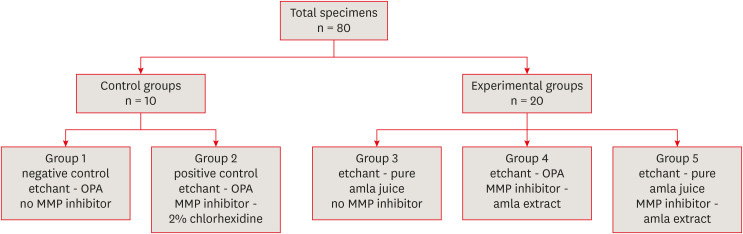
This study aimed to evaluate Emblica officinalis (Indian gooseberry or amla) as an acid etchant and matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) inhibitor, and to compare its effect on the microshear bond strength of composite resin with orthophosphoric acid (OPA) and 2% chlorhexidine (CHX) as an acid etchant and MMP inhibitor, respectively. Materials and MethodsThe etching effect and MMP-inhibiting action of amla on dentin samples were confirmed by scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and gelatin zymography, respectively. Dentinal slabs (3 mm thick) from 80 extracted human molars were divided into 10 and 20 samples to form 2 control groups and 3 experimental groups. Groups 1, 2, and 4 were etched with OPA and groups 3 and 5 with amla juice. An MMP inhibitor was then applied: CHX for group 2 and amla extract for groups 4 and 5. Groups 1 and 3 received no MMP inhibitor. All specimens received a standardized bonding protocol and composite resin build-up, and were subjected to microshear bond strength testing. The force at which the fracture occurred was recorded and statistically analyzed. ResultsAmla juice had a similar etching effect as a self-etch adhesive in SEM and 100% amla extract was found to inhibit MMP-9 by gelatin zymography. The microshear bond strength values of amla were lower than those obtained for OPA and CHX, but the difference was not statistically significant. ConclusionsAmla has a promising role as an acid etchant and MMP inhibitor, but further studies are necessary to substantiate its efficacy.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - In vitro assessment of anti-glioblastoma potential of Emblica officinalis methanolic fruit extract and green nanoparticles in U87-MG cells
Kokkonda Jackson Sugunakara Chary, Anuradha Sharma, Amrita Singh
Medical Oncology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Eco-conscious synthesis of novel 1,2,4-triazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine derivatives as potent Anti-microbial agent and comparative study of cell viability and cytotoxicity in HEK-293 cell line utilizing Indian gooseberry (Phyllanthus emblica) fruit extract
Bhaktiben R. Bhatt, Kamalkishor Pandey, Tarosh Patel, Anupama Modi, Chandani Halpani, Vaibhav D. Bhatt, Bharat C. Dixit
Bioorganic Chemistry.2024; 153: 107936. CrossRef - Cell mediated ECM-degradation as an emerging tool for anti-fibrotic strategy
Peng Zhao, Tian Sun, Cheng Lyu, Kaini Liang, Yanan Du
Cell Regeneration.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Insight into the development of versatile dentin bonding agents to increase the durability of the bonding interface
Isabel Cristina Celerino de Moraes Porto, Teresa de Lisieux Guedes Ferreira Lôbo, Raphaela Farias Rodrigues, Rodrigo Barros Esteves Lins, Marcos Aurélio Bomfim da Silva
Frontiers in Dental Medicine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef
-
1,897
View
-
20
Download
-
4
Web of Science
-
4
Crossref
|