-
In vitro experimental study comparing continuous and intermittent irrigation protocols: influence of sodium hypochlorite volume and contact time on tissue dissolution
-
Alfredo Iandolo, Dina Abdellatif, Davide Mancino, Gwenael Rolin, Camille Coussens, Aurelian Louvrier, Felipe G Belladonna, Edouard Euvrard, Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal da Silva
-
Restor Dent Endod 2025;50(4):e36. Published online October 15, 2025
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2025.50.e36
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
This study aimed to evaluate whether continuous irrigation with larger volumes or allowing sodium hypochlorite (NaOCl) resting time is more critical for pulp tissue dissolution using a controlled artificial root canal system.
Methods
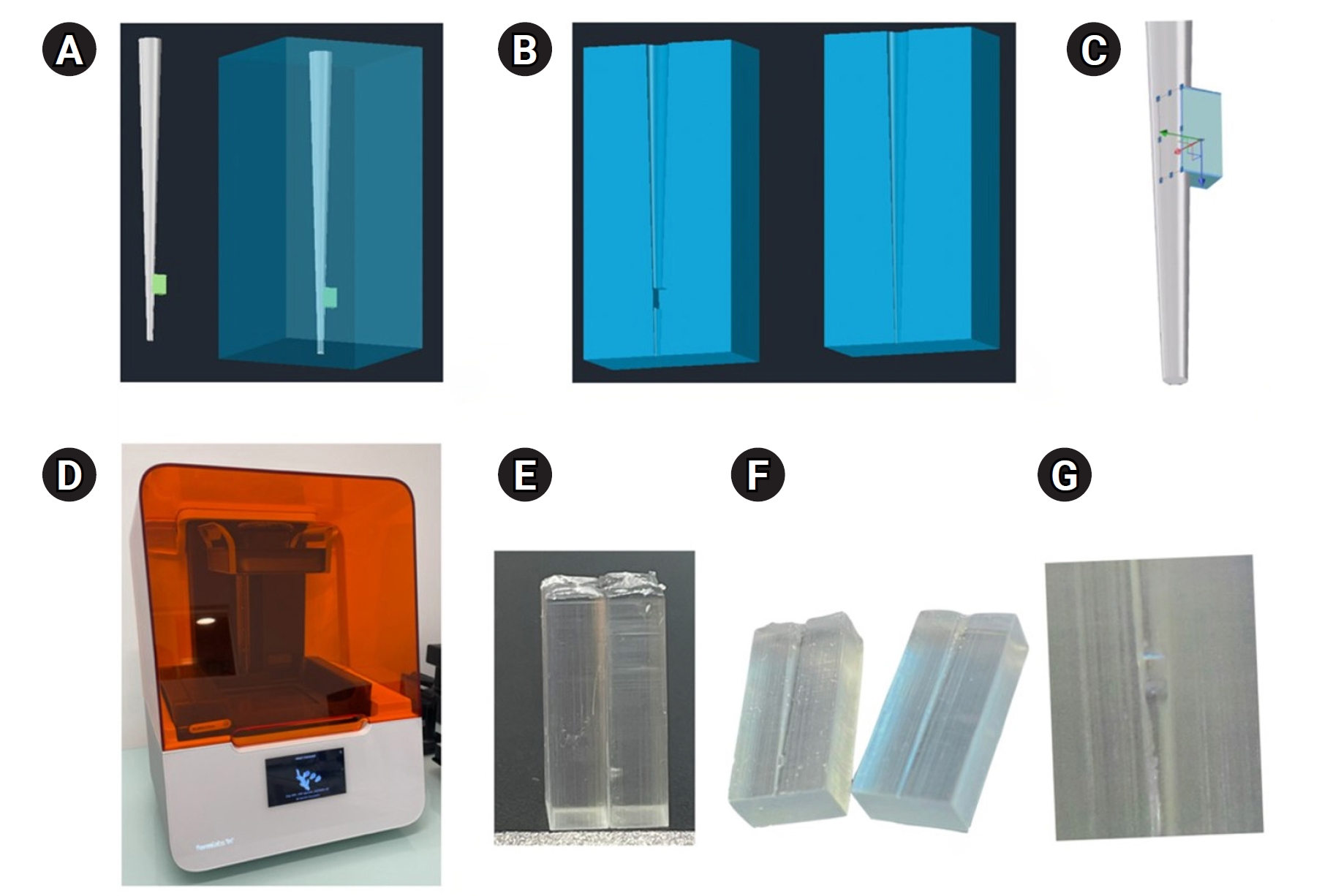
A three-dimensional printed artificial root canal with a lateral canal in the apical third was fabricated. Standardized bovine pulp tissue specimens were inserted, and three irrigation protocols were tested: group A (continuous NaOCl irrigation at 1 mL/min via syringe pump), group B (intermittent NaOCl irrigation with 0.1 mL and a 3-minute resting period), and group C (control, saline irrigation). The time for complete dissolution and the total NaOCl volume were recorded.
Results
Complete dissolution occurred in groups A and B, with significant differences in NaOCl volume and time (p < 0.05). In group A, complete dissolution was consistently observed after the 6th irrigation cycle, corresponding to a total NaOCl volume of 6.0 ± 0.66 mL per test. The average time required for complete dissolution in this group was 6 ± 0.66 minutes. In group B, complete dissolution occurred after the 4th cycle, with a total NaOCl volume of 0.4 ± 0.06 mL per test and a mean dissolution time of 12.6 ± 1.8 minutes.
Conclusions
NaOCl volume and exposure time significantly influence pulp tissue dissolution.
|