-
Periodontal healing following non-surgical repair of an old perforation with pocket formation and oral communication
-
Saeed Asgary, Prashant Verma, Ali Nosrat
-
Restor Dent Endod 2018;43(2):e17. Published online April 13, 2018
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2018.43.e17
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
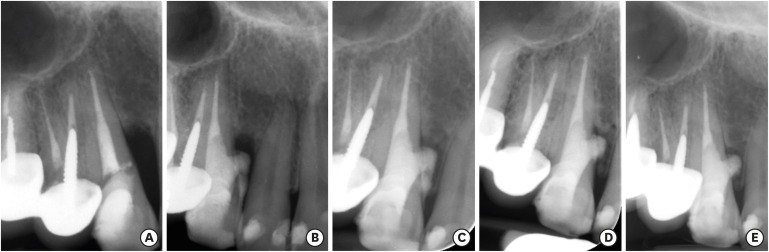
Iatrogenic perforations negatively impact the outcome of endodontic treatments. Studies on prognostic factors showed that perforations in the coronal third of the root with periodontal pocket formation have an unfavorable prognosis. A 36-year-old female was referred for endodontic evaluation of tooth #13 with a history of an iatrogenic perforation, happened 3 years ago. There was a sinus tract associated with perforation, 10 mm probing on the mesial and mesio-palatal, bleeding on probing, radiolucent lesion adjacent to the perforation and complete resorption of the interdental bone between teeth #13 and #12. After the treatment options were discussed, she chose to save the tooth. The tooth was accessed under rubber dam isolation, the perforation site was cleaned and disinfected using 0.5% sodium hypochlorite and sealed with calcium-enriched mixture cement. Eighteen months after treatment the tooth was functional and asymptomatic. The probing depths were normal without bleeding on probing. Radiographically, the interdental crestal bone formed between teeth #13 and #12. Despite all negative prognostic factors in this case (i.e., perforations in the coronal third, pocket formation, and radiolucent lesion), healing was unexpectedly achieved via non-surgical repair of the perforation. Further research on biological aspects of healing in the periodontium following iatrogenic perforations are recommended. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Managing Internal Inflammatory Root Resorption and Perforation of a Mandibular Primary Molar: A Case Report With 15 Months Follow‐Up
Mana Mowji, Motahareh Khosrojerdi
Clinical Case Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Nonsurgical Management of Furcation Defects Using Cervical Sealing With Calcium–Silicate Cements: A Clinical Case Series
Saeed Asgary, Shamimul Hasan
Case Reports in Medicine.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Nonsurgical Management of Simultaneous Double Lateral Root Perforations in Adjacent Teeth Using CBCT and MTA: A Case Report
Beyhan Başkan, Hatice Kübra Başkan, Beyza Güler, Ricardo Faria Ribeiro
Case Reports in Dentistry.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Comprehensive review of composition, properties, clinical applications, and future perspectives of calcium-enriched mixture (CEM) cement: a systematic analysis
Saeed Asgary, Mahtab Aram, Mahta Fazlyab
BioMedical Engineering OnLine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - External Cervical Resorption: A Volumetric Analysis on Evolution of Defects over Time
Ali Nosrat, Omid Dianat, Prashant Verma, Martin D. Levin, Jeffery B. Price, Anita Aminoshariae, Fabio Antonio Piola Rizzante
Journal of Endodontics.2023; 49(1): 36. CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of mineral trioxide aggregate, endoseal, and biodentine in furcation perforation repair
Udita Khare Baralay, Srinidhi Surya Raghavendra
Endodontology.2022; 34(1): 22. CrossRef - Calcium Silicate Cements Application in Lateral Root Perforation Repair: A Case Report with 16-Month Follow-Up
Juan G. Robledo, Pablo A. Rodríguez
Open Journal of Stomatology.2021; 11(08): 317. CrossRef - Vital Pulp Therapy as a Conservative Approach for Management of Invasive Cervical Root Resorption: A Case Series
Saeed Asgary, Mahdieh Nourzadeh, Prashant Verma, M. Lamar Hicks, Ali Nosrat
Journal of Endodontics.2019; 45(9): 1161. CrossRef
-
2,909
View
-
14
Download
-
8
Crossref
-
Surgical management of a failed internal root resorption treatment: a histological and clinical report
-
Saeed Asgary, Mohammad Jafar Eghbal, Leili Mehrdad, Sanam Kheirieh, Ali Nosrat
-
Restor Dent Endod 2014;39(2):137-142. Published online March 21, 2014
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2014.39.2.137
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
This article presents the successful surgical management of a failed mineral trioxide aggregate (MTA) orthograde obturation of a tooth with a history of impact trauma and perforated internal root resorption. A symptomatic maxillary lateral incisor with a history of perforation due to internal root resorption and nonsurgical repair using MTA was referred. Unintentional overfill of the defect with MTA had occurred 4 yr before the initial visit. The excess MTA had since disappeared, and a radiolucent lesion adjacent to the perforation site was evident radiographically. Surgical endodontic retreatment was performed using calcium enriched mixture (CEM) cement as a repair material. Histological examination of the lesion revealed granulation tissue with chronic inflammation, and small fragments of MTA encapsulated within fibroconnective tissue. At the one and two year follow up exams, all signs and symptoms of disease had resolved and the tooth was functional. Complete radiographic healing of the lesion was observed two years after the initial visit. This case report illustrates how the selection of an appropriate approach to treatment of a perforation can affect the long term prognosis of a tooth. In addition, extrusion of MTA into a periradicular lesion should be avoided. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Managing Internal Inflammatory Root Resorption and Perforation of a Mandibular Primary Molar: A Case Report With 15 Months Follow‐Up
Mana Mowji, Motahareh Khosrojerdi
Clinical Case Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Endodontic management of internal replacement resorption of two maxillary central incisors with the aid of cone-beam computed tomography as the diagnostic tool: a case report and review of literature
Fatemeh Eskandari, Safoora Sahebi, Negar Ghorbani Jahandizi, Hossein Mofidi
Journal of Medical Case Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Removal of AH Plus Bioceramic Sealer from Artificial Internal Resorption Cavities Using Different Irrigation Activation Systems
Mine Büker, Meltem Sümbüllü, Emine Şimşek, Fadime Sena Sezer
Cumhuriyet Dental Journal.2025; 28(3): 383. CrossRef - Evaluation of the effectiveness of different supplemental cleaning techniques in the retreatment of roots with small simulated internal resorption cavities: an in vitro comparative study
Sine Güngör Us, Özgür Uzun, Nazlı Merve Güngör
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Comprehensive review of composition, properties, clinical applications, and future perspectives of calcium-enriched mixture (CEM) cement: a systematic analysis
Saeed Asgary, Mahtab Aram, Mahta Fazlyab
BioMedical Engineering OnLine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The various forms of tooth resorption
Jordan Samuel Blum
Australian Endodontic Journal.2024; 50(2): 191. CrossRef - Bioceramics in Endodontics: Updates and Future Perspectives
Xu Dong, Xin Xu
Bioengineering.2023; 10(3): 354. CrossRef - Imaging techniques and various treatment modalities used in the management of internal root resorption: A systematic review
R. S Digholkar, S D Aggarwal, P S Kurtarkar, P. B Dhatavkar, V L Neil, D N Agarwal
Endodontology.2023; 35(2): 85. CrossRef - Treatment of Teeth with Root Resorptions: A Case Report and Systematic Review
Damla Erkal, Abdullah Başoğlu, Damla Kırıcı, Nezahat Arzu Kayar, Simay Koç, Kürşat Er
Galician Medical Journal.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of calcium silicate cements on neuronal conductivity
Derya Deniz-Sungur, Mehmet Ali Onur, Esin Akbay, Gamze Tan, Fügen Daglı-Comert, Taner Cem Sayın
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Mineral trioxide aggregate and other bioactive endodontic cements: an updated overview – part II: other clinical applications and complications
M. Torabinejad, M. Parirokh, P. M. H. Dummer
International Endodontic Journal.2018; 51(3): 284. CrossRef - Periodontal healing following non-surgical repair of an old perforation with pocket formation and oral communication
Saeed Asgary, Prashant Verma, Ali Nosrat
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Conservative Management of Class 4 Invasive Cervical Root Resorption Using Calcium-enriched Mixture Cement
Saeed Asgary, Ali Nosrat
Journal of Endodontics.2016; 42(8): 1291. CrossRef - Importance of CBCT in the management plan of upper canine with internal resorption
Roberto Fornara, Dario Re Cecconi
Giornale Italiano di Endodonzia.2015; 29(2): 70. CrossRef
-
2,242
View
-
14
Download
-
14
Crossref
-
A preliminary report on histological outcome of pulpotomy with endodontic biomaterials vs calcium hydroxide
-
Ali Nosrat, Ali Peimani, Saeed Asgary
-
Restor Dent Endod 2013;38(4):227-233. Published online November 12, 2013
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2013.38.4.227
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
The purpose of the study was to evaluate human dental pulp response to pulpotomy with calcium hydroxide (CH), mineral trioxide aggregate (MTA), and calcium enriched mixture (CEM) cement. Materials and MethodsA total of nine erupted third molars were randomly assigned to each pulpotomy group. The same clinician performed full pulpotomies and coronal restorations. The patients were followed clinically for six months; the teeth were then extracted and prepared for histological assessments. The samples were blindly assessed by an independent observer for pulp vitality, pulp inflammation, and calcified bridge formation. ResultsAll patients were free of clinical signs/symptoms of pulpal/periradicular diseases during the follow up period. In CH group, one tooth had necrotic radicular pulp; other two teeth in this group had vital uninflamed pulps with complete dentinal bridge formation. In CEM cement and MTA groups all teeth had vital uninflamed radicular pulps. A complete dentinal bridge was formed beneath CEM cement and MTA in all roots. Odontoblast-like cells were present beneath CEM cement and MTA in all samples. ConclusionsThis study revealed that CEM cement and MTA were reliable endodontic biomaterials in full pulpotomy treatment. In contrast, the human dental pulp response to CH might be unpredictable.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Long-term Outcome of Vital Pulp Therapy and Regenerative Endodontic Procedures in Immature Permanent Maxillary Incisors: A 7-year Follow-up Case Report
Mulham Almaliki, Motaz Almaghraby, Abdulaziz Bakhsh
International Journal of Clinical Pediatric Dentistry.2026; 19(3): 403. CrossRef - A meta‐analysis of calcium silicate‐based cements and calcium hydroxide as promoters of hard tissue bridge formation
Emmanuel J. N. L. Silva, Karem P. Pinto, Fernanda N. S. J. Riche, Maristela G. H. Carestiato, Jorge N. R. Martins, Henry F. Duncan, Marco A. Versiani, Gustavo De‐Deus
International Endodontic Journal.2025; 58(5): 685. CrossRef - Clinical and radiographic outcomes of pulpotomy materials in permanent teeth: a systematic review of calcium hydroxide, MTA, biodentine, and iRoot BP plus
Anggi Putri Riandani, Arief Cahyanto, Rana Abdelbaset Lotfy Diab, Ratih Widyasari, Atia Nurul Sidiqa, Hendra Dian Adhita Dharsono, Myrna Nurlatifah Zakaria
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Comprehensive review of composition, properties, clinical applications, and future perspectives of calcium-enriched mixture (CEM) cement: a systematic analysis
Saeed Asgary, Mahtab Aram, Mahta Fazlyab
BioMedical Engineering OnLine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Hard tissue formation in pulpotomized primary teeth in dogs with nanomaterials MCM-48 and MCM-48/hydroxyapatite: an in vivo animal study
Sahar Talebi, Nosrat Nourbakhsh, Ardeshir Talebi, Amir Abbas Nourbakhsh, Abbas Haghighat, Maziar Manshayi, Hamid Reza Bakhsheshi, Razieh Karimi, Rahman Nazeri, Kenneth J.D. Mackenzie
BMC Oral Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The Role of Growth Factor Delivery Systems on Cellular Activities of Dental
Stem Cells: A Systematic Review (Part II)
Sayna Shamszadeh, Armin Shirvani, Saeed Asgary
Current Stem Cell Research & Therapy.2024; 19(4): 587. CrossRef - Calcium Silicate-Based Cements in Restorative Dentistry: Vital Pulp Therapy Clinical, Radiographic, and Histological Outcomes on Deciduous and Permanent Dentition—A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Maria Teresa Xavier, Ana Luísa Costa, João Carlos Ramos, João Caramês, Duarte Marques, Jorge N. R. Martins
Materials.2024; 17(17): 4264. CrossRef - Pulpotomy: An alternative treatment modality to conventional root canal treatment
Günther Streit, Martin Vorster, Peet J Van der Vyver
South African Dental Journal.2023; 78(06): 309. CrossRef - A Comparative Histological Analysis of Human Pulp Following Direct Pulp Capping with Propolis or Biodentine
Nehad A Ahmad, Nevin A. Gad, Marwa H. Abdulmonaem
Journal of Nature and Science of Medicine.2022; 5(3): 281. CrossRef - Expression of Matrix Metalloproteinases-8 and Myeloperoxidase in Pulp Tissue after Pulpotomy with Calcium Silicate Cements
Nayara Nery de Oliveira Cunha, Marina Azevedo Junqueira, Leopoldo Cosme-Silva, Laís da Silveira Terra Santos, George Augusto Veloso de Oliveira, Rafael Tobias Moretti Neto, Denismar Alves Nogueira, Maísa Ribeiro Pereira Lima Brigagão, Ana Beatriz da Silve
Pesquisa Brasileira em Odontopediatria e Clínica Integrada.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Long-term Outcomes of Full Pulpotomy in Permanent Molars for Patients Treated in a Single, Short Session under Special Conditions
Natacha Linas, Nicolas Decerle, Marie-Laure Munoz-Sanchez, Denise Faulks, Valérie Collado, Emmanuel Nicolas, Martine Hennequin, Pierre-Yves Cousson
Journal of Endodontics.2020; 46(11): 1597. CrossRef - Quantitative Assessment of Root Development after Regenerative Endodontic Therapy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Teng Kai Ong, Ghee Seong Lim, Maharaj Singh, Alissa V. Fial
Journal of Endodontics.2020; 46(12): 1856. CrossRef - Dexamethasone- loaded polymeric porous sponge as a direct pulp capping agent
Amjad Alagha, Abdulwahab Nourallah, Sahar Alhariri
Journal of Biomaterials Science, Polymer Edition.2020; 31(13): 1689. CrossRef - Postendodontic Pain after Pulpotomy or Root Canal Treatment in Mature Teeth with Carious Pulp Exposure: A Multicenter Randomized Controlled Trial
Mohammad Jafar Eghbal, Ali Haeri, Arash Shahravan, Ali Kazemi, Fariborz Moazami, Mohammad Ali Mozayeni, Eshaghali Saberi, Mohammad Samiei, Mehdi Vatanpour, Alireza Akbarzade Baghban, Mahta Fazlyab, Ardavan Parhizkar, Mahboobe Ahmadi, Nazila Akbarian Rad,
Pain Research and Management.2020; 2020: 1. CrossRef - Vital Pulp Therapy as a Conservative Approach for Management of Invasive Cervical Root Resorption: A Case Series
Saeed Asgary, Mahdieh Nourzadeh, Prashant Verma, M. Lamar Hicks, Ali Nosrat
Journal of Endodontics.2019; 45(9): 1161. CrossRef - Which procedures and materials could be applied for full pulpotomy in permanent mature teeth? A systematic review
M. Zanini, M. Hennequin, PY. Cousson
Acta Odontologica Scandinavica.2019; 77(7): 541. CrossRef - Periodontal healing following non-surgical repair of an old perforation with pocket formation and oral communication
Saeed Asgary, Prashant Verma, Ali Nosrat
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Mineral trioxide aggregate and other bioactive endodontic cements: an updated overview – part I: vital pulp therapy
M. Parirokh, M. Torabinejad, P. M. H. Dummer
International Endodontic Journal.2018; 51(2): 177. CrossRef - Treatment Outcomes of 4 Vital Pulp Therapies in Mature Molars
Saeed Asgary, Raheleh Hassanizadeh, Hassan Torabzadeh, Mohammad Jafar Eghbal
Journal of Endodontics.2018; 44(4): 529. CrossRef - A Review of Criteria for the Evaluation of Pulpotomy Outcomes in Mature Permanent Teeth
Marjorie Zanini, Martine Hennequin, Pierre-Yves Cousson
Journal of Endodontics.2016; 42(8): 1167. CrossRef - Calcium-Enriched Mixture Pulpotomy of Primary Molar Teeth with Irreversible Pulpitis. A Clinical Study
Mahtab Memarpour, Soleiman Fijan, Saeed Asgary, Marzieh Keikhaee
The Open Dentistry Journal.2016; 10(1): 43. CrossRef - Endodontie in der unreifen bleibenden Dentition — Maßnahmen zur Vitalerhaltung, Apexifikation und Regeneration der Pulpa
Martin Jung
Oralprophylaxe & Kinderzahnheilkunde.2016; 38(1): 29. CrossRef - Conservative Management of Class 4 Invasive Cervical Root Resorption Using Calcium-enriched Mixture Cement
Saeed Asgary, Ali Nosrat
Journal of Endodontics.2016; 42(8): 1291. CrossRef - Permanent teeth pulpotomy survival analysis: retrospective follow-up
Gustavo Golgo Kunert, Itaborai Revoredo Kunert, Luiz Cesar da Costa Filho, José Antônio Poli de Figueiredo
Journal of Dentistry.2015; 43(9): 1125. CrossRef - Cytocompatibility and Antibacterial Properties of Capping Materials
Claudio Poggio, Carla Renata Arciola, Riccardo Beltrami, Annachiara Monaco, Alberto Dagna, Marco Lombardini, Livia Visai
The Scientific World Journal.2014; 2014: 1. CrossRef - Surgical management of a failed internal root resorption treatment: a histological and clinical report
Saeed Asgary, Mohammad Jafar Eghbal, Leili Mehrdad, Sanam Kheirieh, Ali Nosrat
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2014; 39(2): 137. CrossRef - Effect of Mineral Trioxide Aggregate Surface Treatments on Morphology and Bond Strength to Composite Resin
Joo-Hee Shin, Ji-Hyun Jang, Sang Hyuk Park, Euiseong Kim
Journal of Endodontics.2014; 40(8): 1210. CrossRef
-
2,164
View
-
14
Download
-
27
Crossref
-
Evaluation of the effect of blood contamination on the compressive strength of MTA modified with hydration accelerators
-
Kaveh Oloomi, Eshaghali Saberi, Hadi Mokhtari, Hamid Reza Mokhtari Zonouzi, Ali Nosrat, Mohammad Hossein Nekoofar, Paul Michael Howell Dummer
-
Restor Dent Endod 2013;38(3):128-133. Published online August 23, 2013
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2013.38.3.128
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
This study was performed to evaluate the effect of blood contamination on the compressive strength (CS) of Root MTA (RMTA) modified with Calcium chloride (CaCl2) and Disodium hydrogen phosphate (Na2HPO4) as setting accelerators over time. Materials and MethodsA total of 110 cylindrical specimens of RMTA were divided into 6 experimental groups as follows: Group1, RMTA; Group 2, RMTA modified with CaCl2 (RMTA-C); Group 3, RMTA modified with Na2HPO4 (RMTA-N); Group 4, RMTA contaminated with blood; Group 5, RMTA-C contaminated with blood; Group 6, RMTA-N contaminated with blood. The CS of specimens in all groups was evaluated after 3 hr, 24 hr, and 1 wk. In the modified groups (groups 2, 3, 5, and 6) the CS of five specimens per group was also evaluated after 1 hr. ResultsBlood contamination significantly reduced the CS of all materials at all time intervals (p < 0.05). After 3 hr, the CS of specimens in the RMTA groups (with and without blood contamination) was significantly lower than those in the RMTA-C and RMTA-N groups (p < 0.05). The CS values were not significantly different at the other time intervals. In all groups, the CS of specimens significantly increased over time (p < 0.05). ConclusionsBlood contamination decreased the CS of both original and accelerated RMTA.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - A comparative evaluation of setting time in the presence of blood contamination of four root end filling biomaterials (MTA angelus, biodentine, endosequence root repair material, bio-C repair) An in-vitro study
Damini Kesarwani, Sunandan Mittal, Tarun Kumar, Vanita Keshav, Vidushi Gilhotra, Arisha Jain
Endodontology.2026; 38(1): 50. CrossRef - The effect of three additives on properties of mineral trioxide aggregate cements: a systematic review and meta-analysis of in vitro studies
Behnam Bolhari, Faranak Noori, Hadi Assadian, Amir Raee, Sholeh Ghabraei, Ahmad-Reza Shamshiri, Artak Heboyan
BMC Oral Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Push‐out bond strength of the calcium silicate‐based endodontic cements in the presence of blood: A systematic review and meta‐analysis of in vitro studies
Mahdieh Alipour, Leili Faraji Gavgani, Negin Ghasemi
Clinical and Experimental Dental Research.2022; 8(2): 571. CrossRef - Effect of bioactive glass addition on the physical properties of mineral trioxide aggregate
Jei Kim, Hyun-Jung Kim, Seok Woo Chang, Soram Oh, Sun-Young Kim, Kyoung-Kyu Choi, Duck-Su Kim, Ji-Hyun Jang
Biomaterials Research.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of the addition of nanoparticles of CaCO3 and different water‐to‐powder ratios on the physicochemical properties of white Portland cement
Cleonice da Silveira Teixeira, Jessica Coelho Wasielewsky, Giovanna Slongo dos Santos, Anarela Bernardi, Eduardo Antunes Bortoluzzi, Lucas da Fonseca Roberti Garcia
Microscopy Research and Technique.2021; 84(4): 592. CrossRef - Assessment of the interaction of Portland cement-based materials with blood and tissue fluids using an animal model
P. Schembri Wismayer, C. Y. K. Lung, F. Rappa, F. Cappello, J. Camilleri
Scientific Reports.2016;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of the plant-based hemostatic agent Ankaferd Blood Stopper® on the biocompatibility of mineral trioxide aggregate
Muzaffer Emir Dinçol, Hakan Ozbas, Bulent Yılmaz, Handan Ersev, Selcuk Gokyay, Vakur Olgac
BMC Oral Health.2016;[Epub] CrossRef - Surface microhardness of three thicknesses of mineral trioxide aggregate in different setting conditions
Noushin Shokouhinejad, Leila Jafargholizadeh, Mehrfam Khoshkhounejad, Mohammad Hossein Nekoofar, Maryam Raoof
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2014; 39(4): 253. CrossRef - Surgical management of a failed internal root resorption treatment: a histological and clinical report
Saeed Asgary, Mohammad Jafar Eghbal, Leili Mehrdad, Sanam Kheirieh, Ali Nosrat
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2014; 39(2): 137. CrossRef
-
1,917
View
-
4
Download
-
9
Crossref
|