-
The influence of nanofillers on the properties of ethanol-solvated and non-solvated dental adhesives
-
Leonardo Bairrada Tavares da Cruz, Marcelo Tavares Oliveira, Cintia Helena Coury Saraceni, Adriano Fonseca Lima
-
Restor Dent Endod 2019;44(3):e28. Published online July 24, 2019
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2019.44.e28
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
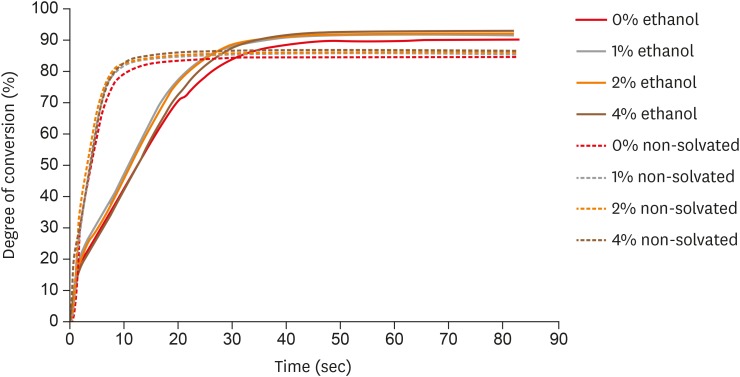
The aim of this study was to evaluate the influence of different concentrations of nanofillers on the chemical and physical properties of ethanol-solvated and non-solvated dental adhesives. Materials and MethodsEight experimental adhesives were prepared with different nanofiller concentrations (0, 1, 2, and 4 wt%) and 2 solvent concentrations (0% and 10% ethanol). Several properties of the experimental adhesives were evaluated, such as water sorption and solubility (n = 5, 20 seconds light activation), real-time degree of conversion (DC; n = 3, 20 and 40 seconds light activation), and stability of cohesive strength at 6 months (CS; n = 20, 20 seconds light activation) using the microtensile test. A light-emitting diode (Bluephase 20i, Ivoclar Vivadent) with an average light emittance of 1,200 mW/cm2 was used. ResultsThe presence of solvent reduced the DC after 20 seconds of curing, but increased the final DC, water sorption, and solubility of the adhesives. Storage in water reduced the strength of the adhesives. The addition of 1 wt% and 2 wt% nanofillers increased the polymerization rate of the adhesives. ConclusionsThe presence of nanofillers and ethanol improved the final DC, although the DC of the solvated adhesives at 20 seconds was lower than that of the non-solvated adhesives. The presence of ethanol reduced the strength of the adhesives and increased their water sorption and solubility. However, nanofillers did not affect the water sorption and strength of the tested adhesives.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - In Vitro Comparison of Gingival Epithesis Materials: Color Stability, Surface Properties, and Microbial Adhesion After Staining
Ellen Pick, Andrea Gubler, Thomas Attin, Patrick R. Schmidlin
Dentistry Journal.2026; 14(3): 142. CrossRef - Effect of boric acid on the color stability and mechanical properties of 3D-printed permanent resins
Dalndushe Abdulai, Rafat Sasany, Raghib Suradi, Mehran Moghbel, Seyed Ali Mosaddad
Scientific Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Development of a Boron Nitride-Filled Dental Adhesive System
Senthilguru Kulanthaivel, Jeremiah Poppen, Sandra Ribeiro Cunha, Benjamin Furman, Kyumin Whang, Erica C. Teixeira
Polymers.2023; 15(17): 3512. CrossRef - Analyses of Experimental Dental Adhesives Based on Zirconia/Silver Phosphate Nanoparticles
Abdul Khan, Yasmin Alhamdan, Hala Alibrahim, Khalid Almulhim, Muhammad Nawaz, Syed Ahmed, Khalid Aljuaid, Ijlal Ateeq, Sultan Akhtar, Mohammad Ansari, Intisar Siddiqui
Polymers.2023; 15(12): 2614. CrossRef - Mechanical characterization and adhesive properties of a dental adhesive modified with a polymer antibiotic conjugate
Camila Sabatini, Russell J. Aguilar, Ziwen Zhang, Steven Makowka, Abhishek Kumar, Megan M. Jones, Michelle B. Visser, Mark Swihart, Chong Cheng
Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials.2022; 129: 105153. CrossRef
-
1,534
View
-
9
Download
-
5
Crossref
-
Effects of radiant exposure and wavelength spectrum of light-curing units on chemical and physical properties of resin cements
-
Adriano Fonseca Lima, Stephanie Ellen Ferreira Formaggio, Lígia França Aires Zambelli, Alan Rodrigo Muniz Palialol, Giselle Maria Marchi, Cintia Helena Coury Saraceni, Marcelo Tavares de Oliveira
-
Restor Dent Endod 2016;41(4):271-277. Published online September 26, 2016
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2016.41.4.271
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
In this study, we evaluated the influence of different radiant exposures provided by single-peak and polywave light-curing units (LCUs) on the degree of conversion (DC) and the mechanical properties of resin cements. Materials and MethodsSix experimental groups were established for each cement (RelyX ARC, 3M ESPE; LuxaCore Dual, Ivoclar Vivadent; Variolink, DMG), according to the different radiant exposures (5, 10, and 20 J/cm2) and two LCUs (single-peak and polywave). The specimens were made (7 mm in length × 2 mm in width × 1 mm in height) using silicone molds. After 24 hours of preparation, DC measurement was performed using Fourier transform infrared spectrometry. The same specimens were used for the evaluation of mechanical properties (flexural strength, FS; elastic modulus, E) by a three-point bending test. Data were assessed for normality, after which two-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) and post hoc Tukey's test were performed. ResultsNo properties of the Variolink cement were influenced by any of the considered experimental conditions. In the case of the RelyX ARC cement, DC was higher when polywave LCU was used; FS and E were not influenced by the conditions evaluated. The LuxaCore cement showed greater sensitivity to the different protocols. ConclusionsOn the basis of these results, both the spectrum of light emitted and the radiant exposure used could affect the properties of resin cements. However, the influence was material-dependent.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Efficiency and limitations of polywave light-curing units in restorative dentistry: a systematic review
Eduardo Fernández Godoy, Alain Chaple Gil, Rodrigo Caviedes Thomas, Cristian Bersezio Miranda, Javier Martín Casielles, Gonzalo Rodríguez Martínez, Pablo Angel Aguirre
Clinical Oral Investigations.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Light Transmittance and Depth of Cure of a Bulk Fill Composite Based on the Exposure Reciprocity Law
Mateus Garcia Rocha, Jean-François Roulet, Mario Alexandre Coelho Sinhoreti, Américo Bortolazzo Correr, Dayane Oliveira
Brazilian Dental Journal.2021; 32(1): 78. CrossRef
-
1,865
View
-
4
Download
-
2
Crossref
-
Antioxidant therapy enhances pulpal healing in bleached teeth
-
Adriano Fonseca Lima, Marcelo Rocha Marques, Diana Gabriela Soares, Josimeri Hebling, Giselle Maria Marchi, Carlos Alberto de Souza Costa
-
Restor Dent Endod 2016;41(1):44-54. Published online February 1, 2016
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2016.41.1.44
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the histopathological effects of an antioxidant therapy on the pulp tissue of rat teeth exposed to a bleaching gel with 35% hydrogen peroxide. Materials and MethodsForty rats were subjected to oral ingestion by gavage of distilled water (DW) or ascorbic acid (AA) 90 min before the bleaching therapy. For the bleaching treatment, the agent was applied twice for 5 min each to buccal surfaces of the first right mandibular molars. Then, the animals were sacrificed at 6 hr, 24 hr, 3 day, or 7 day post-bleaching, and the teeth were processed for microscopic evaluation of the pulp tissue. ResultsAt 6 hr, the pulp tissue showed moderate inflammatory reactions in all teeth of both groups. In the DW and AA groups, 100% and 80% of teeth exhibited pulp tissue with significant necrosis and intense tissue disorganization, respectively. At 24 hr, the AA-treated group demonstrated a greater regenerative capability than the DW group, with less intense inflammatory reaction and new odontoblast layer formation in 60% of the teeth. For up to the 7 day period, the areas of pulpal necrosis were replaced by viable connective tissue, and the dentin was underlined by differentiated odontoblast-like cells in most teeth of both groups. ConclusionsA slight reduction in initial pulpal damage during post-bleaching was promoted by AA therapy. However, the pulp tissue of AA-treated animals featured faster regenerative potential over time.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Influence of dental bleaching on the pulp tissue: A systematic review of in vivo studies
Mariana Viana Donato, Alexandre Henrique dos Reis‐Prado, Lucas Guimarães Abreu, Lara Cancella de Arantes, Juliana Goto, Hebertt Gonzaga dos Santos Chaves, Luciano Tavares Angelo Cintra, André Luiz Fraga Briso, Isabella Faria da Cunha Peixoto, Francine Ben
International Endodontic Journal.2024; 57(6): 630. CrossRef - ANALYSIS OF THE INFLUENCE OF THE TEETH WHITENING PROCEDURE ON THE GUM AND CYTOKINE PROFILE OF ORAL FLUID (LITERATURE REVIEW)
S. S. Bozhik, N. V. Hasyuk, V. B. Radchuk
Bulletin of Problems Biology and Medicine.2024; 1(3): 17. CrossRef - Assessing the Viability of Laser-Activated Dental Bleaching Compared to Conventional In-Office Bleaching Methods: A Systematic Review of Clinical and In Vitro Studies
Eugenia Anagnostaki, Valina Mylona, Steven Parker, Mark Cronshaw, Martin Grootveld
Applied Sciences.2023; 13(22): 12459. CrossRef - Effects of the application of sodium ascorbate after in-office bleaching on the penetration of hydrogen peroxide, color change, and microtensile bond strength
Alexandra Mena-Serrano, María G. Granda-Albuja, Jenny Naranjo, Eliana Aldás Fierro, Michael Willian Favoreto, Alessandro D. Loguercio, Alessandra Reis
Brazilian Dental Journal.2023; 34(5): 87. CrossRef - Can different agents reduce the damage caused by bleaching gel to pulp tissue? A systematic review of basic research
Letícia Aparecida Silva Batista, Alexandre Henrique dos Reis-Prado, Hebertt Gonzaga dos Santos Chaves, Lara Cancella de Arantes, Luís Fernando Santos Alves Morgan, Carolina Bosso André, Thaís Yumi Suzuki, Francine Benetti
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Design of a thermosensitive ibuprofen-loaded nanogel as smart material applied as anti-inflammatory in tooth bleaching: An in vivo study
Samara K.S.C.F. Moura, Milena L.V. dos Santos, Lucas A. do Nascimento, Mariana F.A. da Silva, Glória M. de França, Lucas M. da Costa, Aldo C. Medeiros, Raimundo F. Araújo-Júnior, Aurigena A. de Araújo, Cláudia N. Oliveira, André L. Dorini, Rejane A. de Ca
Journal of Drug Delivery Science and Technology.2022; 68: 103123. CrossRef - Effect of bleaching gel volume on color change and postoperative sensitivity: a randomized clinical study
Lara Maria Bueno Esteves, Paulo Henrique dos Santos, Ticiane Cestari Fagundes, Marjorie de Oliveira Gallinari, Giulia Bessa de Mello Antonaccio, Luciano Tavares Ângelo Cintra, André Luiz Fraga Briso
Clinical Oral Investigations.2022; 26(3): 2527. CrossRef - Human Dental Pulp Stem Cells Exhibit Different Biological Behaviours in Response to Commercial Bleaching Products
Carmen Llena, Mar Collado-González, Christopher Joseph Tomás-Catalá, David García-Bernal, Ricardo Elías Oñate-Sánchez, Francisco Javier Rodríguez-Lozano, Leopoldo Forner
Materials.2018; 11(7): 1098. CrossRef - Concentration‐dependent effect of bleaching agents on the immunolabelling of interleukin‐6, interleukin‐17 and CD5‐positive cells in the dental pulp
F. Benetti, J. E. Gomes‐Filho, L. L. Ferreira, G. Sivieri‐Araújo, E. Ervolino, A. L. F. Briso, L. T. A. Cintra
International Endodontic Journal.2018; 51(7): 789. CrossRef
-
1,684
View
-
6
Download
-
9
Crossref
|