Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > Restor Dent Endod > Volume 34(5); 2009 > Article
- Original Article The effect of concentration and application time of hydrogen peroxide on the microtensile bond strength of resin restorations to the dentin at different depths
- Jeong-Lyong Son, Gye-Young Lee, Yu-Mi Kang, Young-Taek Oh, Kwang-Won Lee, Tae-Gun Kim
-
2009;34(5):-414.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2009.34.5.406
Published online: September 30, 2009
Department of Conservative Dentistry, School of Dentistry, Chonbuk National University, Korea.
- Corresponding Author: Tae-Gun Kim. Department of Conservative Dentistry, School of Dentistry, Chonbuk National University, Geumam-Dong, Deokjin-Gu, Jeonju, Jeonbuk, 561-712, Korea. Tel: 82-63-250-2319, Fax: 82-63-250-2049, banana994404@daum.net
• Received: June 18, 2009 • Revised: July 16, 2009 • Accepted: September 2, 2009
Copyright © 2009 The Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry
- 1,145 Views
- 3 Download
- 1 Crossref
Abstract
-
The purpose of this study was to examine the effect of hydrogen peroxide at different application time and concentrations on the microtensile bond strength of resin restorations to the deep and the pulp chamber dentin.A conventional endodontic access cavity was prepared in each tooth, and then the teeth were randomly divided into 1 control group and 4 experimental groups as follows: Group 1, non treated; Group 2, with 20% Hydrogen peroxide(H2O2); Group 3, with 10% H2O2; Group 4, with 5% H2O2; Group 5, with 2.5% H2O2; the teeth of all groups except group 1 were treated for 20, 10, and 5min. The treated teeth were filled using a Superbond C&B (Sun medical Co., Shiga, Japan). Thereafter, the specimens were stored in distilled water at 37℃ for 24-hours and then sectioned into the deep and the chamber dentin. The microtensile bond strength values of each group were analyzed by 3-way ANOVA and Tukey post hoc test(p < 0.05).In this study, the microtensile bond strength of the deep dentin (D1) was significantly greater than that of the pulp chamber dentin (D2) in the all groups tested. The average of microtensile bond strength was decreased as the concentration and the application time of H2O2 were increased. Analysis showed significant correlation effect not only between the depth of the dentin and the concentration of H2O2 but also between the concentration of H2O2 and the application time(p < 0.05), while no significant difference existed among these three variables(p > 0.05). The higher H2O2 concentration, the more opened dentinal tubules under a scanning electron microscope(SEM) examination.
- 1. Oliveira DP, Teixeira ECN, Ferraz CCR, Teixeira FB. Effect of intracoronal bleaching agents on dentin microhardness. J Endod. 2007;33(4):460-462.ArticlePubMed
- 2. Chng HK, Palamara JEA, Messer HH. Effect of hydrogen peroxide and sodium perborate on biomechanical properties of human dentin. J Endod. 2002;28(2):62-67.ArticlePubMed
- 3. Jiang T, Ma X, Wang Y, Zhu Z, Tong H, Hu J. Effects of hydrogen peroxide on human dentin structure. J Dent Res. 2007;86(11):1040-1045.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 4. Spasser HF. A simple bleaching technique using sodium perborate. NY State Dent J. 1961;27: 332-334.
- 5. Nutting EB, Poe GS. A new combination for bleaching teeth. J South Calif Dent Assoc. 1963;31: 289-291.
- 6. Choi SH, No BD, Park SH, Lee SJ. The effect of intracanal base on prevention of apical leakage of bleaching agents. J Korean Acad Conserv Dent. 1999;24(3):453-464.
- 7. Lai SCN, Mak YF, Cheung G, Osorio R, Toledano M, Carvalho RM, Tay FR, Pashley DH. Reversal of compromised bonding to oxidized etched dentin. J Dent Res. 2001;80(10):1919-1924.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 8. Kawamoto K, Tsujimoto Y. Effects of the hydroxyl radical and hydrogen peroxide on tooth bleaching. J Endod. 2004;30(1):45-50.ArticlePubMed
- 9. Heling I, Parson A, Rostein I. Effect of bleaching agents on dentin permeability to Streptococcus faecalis. J Endod. 1995;21: 540-542.ArticlePubMed
- 10. Madison S, Walton R. Cervical root resorption following bleaching of endodontically treated teeth. J Endod. 1990;16: 570-574.ArticlePubMed
- 11. Timpawat S, Nipattamanon C, Kijsamanmith K, Messer HH. Effect of bleaching agents on bonding to pulp chamber dentine. Int Endod J. 2005;38: 211-217.ArticlePubMed
- 12. Dias W, Pereira P, Swift EJ. Effect of bur type on microtensile bond strengths of self-etching systems to human dentin. J Adhes Dent. 2004;6: 195-203.PubMed
- 13. Park SH. The role of collagen fiber in dentin bonding. J Korean Acad Conserv Dent. 1997;22(1):470-478.
- 14. Nikaido T, Takano Y, Sasafuchi Y, Burrow MF, Tagami J. Bond strengths to endodontically treated teeth. Am J Dent. 1999;12: 177-180.PubMed
- 15. Kim KG, Park JW. Comparison of shear bond strength of different bonding systems on bleached enamel. J Korean Acad Conserv Dent. 2004;29(1):30-35.Article
- 16. Spyrides GM, Perdigao J, Araujo M, Spyrides SMM. Effect of whitening agents on dentin bonding. J Esthet Dent. 2000;12: 264-270.ArticlePubMed
- 17. Torneck CD, Titley KC, Smith DC, Adibfar A. Adhesion of light-cured composite resin to bleached and unbleached bovine dentin. Endod Dent Traumatol. 1990;6: 97-103.ArticlePubMed
- 18. Erdemir A, Ari H, Güngüneş H, Belli S. Effect of medications for root canal treatment on bonding to root canal dentin. J Endod. 2004;30(2):113-116.ArticlePubMed
- 19. Titley KC, Torneck CD, Ruse ND. The effect of carbamide-peroxide gel on the shear bond strength of a microfil resin to bovine enamel. J Dent Res. 1992;71(1):20-24.PubMed
- 20. Titley KC, Torneck CD, Ruse ND, Krmec D. Adhesion of a resin composite to bleached and unbleached human enamel. J Endod. 1993;19(3):112-115.ArticlePubMed
- 21. Joiner A. Review of the effects of peroxide on enamel and dentin properties. J Dent. 2007;35: 889-896.PubMed
- 22. Sulieman M, Addy M, Macdonald E, Rees JS. A safety study in vitro for the effects of an in-office bleaching system on the integrity of enamel and dentine. J Dent. 2004;32: 581-590.ArticlePubMed
- 23. Duschner H, Gotz H, White DJ, Kozak KM, Zoladz JR. Effects of hydrogen peroxide bleaching strips on tooth surface colour, surface microhardness, surface and subsurface ultrastructure, and micro- chemical (Raman Spectroscopic) composition. J Clin Dent. 2006;17: 72-78.PubMed
- 24. Joiner A, Thakker G, Cooper Y. Evaluation of a 6% hydrogen peroxide tooth whitening gel on enamel and dentine microhardness in vitro. J Dent. 2004;32: 27-34.Article
- 25. Zalkind M, Arwaz JR, Goldman A, Rotstein I. Surface morphology changes in human enamel, dentin and cementum following bleaching, a scanning electron microscopy study. Endod Dent Traumatol. 1996;12: 82-88.ArticlePubMed
- 26. Surapipongpuntr P, Duangcharee W, Kwangsamai S, Ekka A. Effect of root canal irrigants on cervical dentine permeability to hydrogen peroxide. Int Endod J. 2008;41: 821-827.ArticlePubMed
REFERENCES
Figure 4
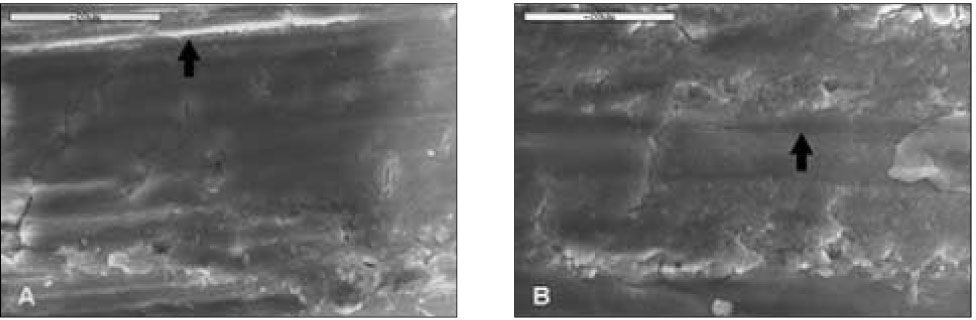
Control group(2K). Most surface was covered with smear layer and had scratches (black arrow) due to using a diamond bur. A. D1, B. D2, Bar=20µm.

Figure 5
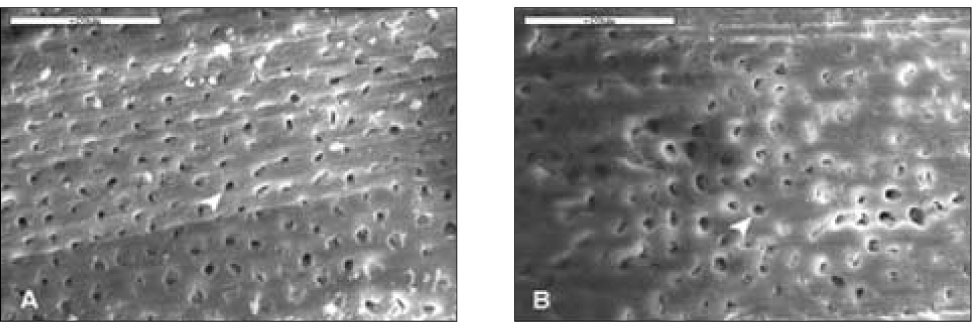
With 20% H2O2 for 20min(2K). Dentinal tubules (white arrow head) were opened completely and the smear layer scarcely remained. A. D1, B. D2, Bar=20µm.

Figure 6
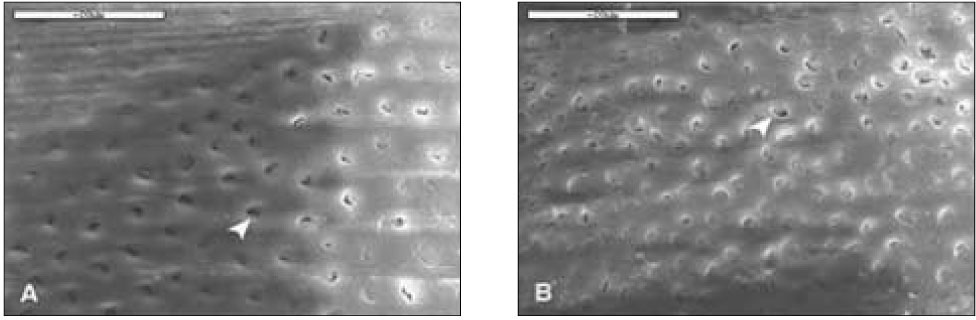
With 10% H2O2 for 20min(2K). Dentinal tubules (white arrow head) were opened in a part and the smear layer remained. A. D1, B. D2, Bar=20µm.

Figure 7
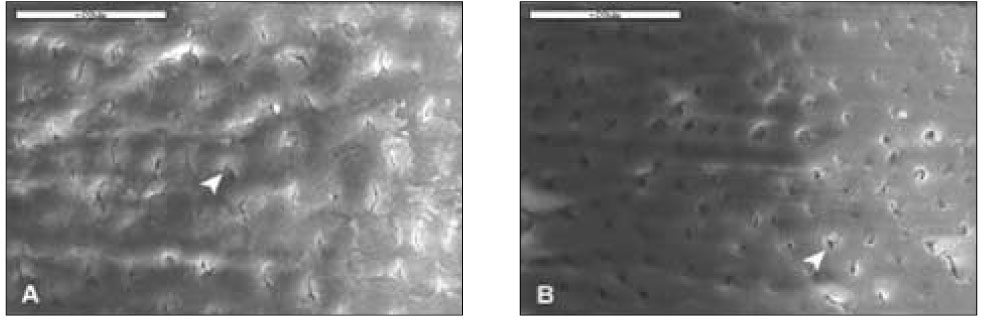
With 5% H2O2 for 20min(2K). A. D1, Dentinal tubules (white arrow head) were obscure and covered with the smear layer; B. D2, Dentinal tubules were clear and opened in a part. Bar=20µm.

Figure 8
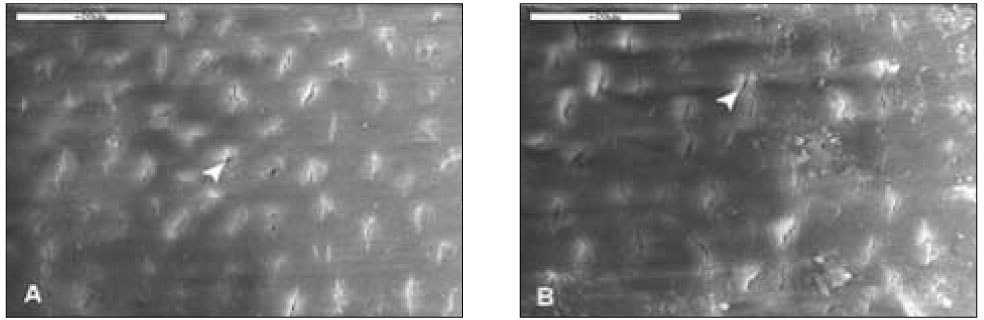
With 2.5% H2O2 for 20min(2K). Dentinal tubules (white arrow head) were obscure and covered with the smear layer. A: D1; B: D2; the surface of D1 and D2 had a similar pattern; Bar=20µm.

Table 1
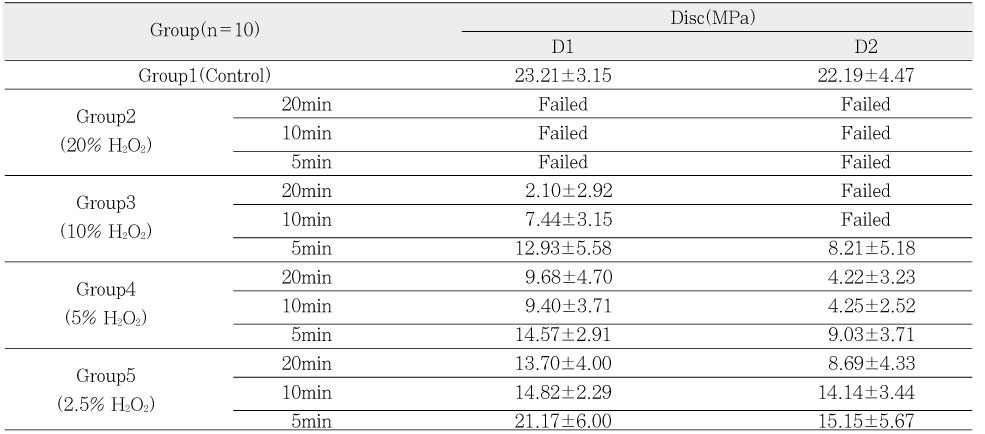
Averages of the microtensile bond strength to the deep and the pulp chamber dentin by H2O2 concentration and application time(Mean±SD).

Tables & Figures
REFERENCES
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by 

- Changes in µ-TBS to pulp chamber dentin after the application of NaOCl & reversal effect by using sodium ascorbate
Su-Mi Kwon, Tae-Gun Kim, Mi-Kyung Yu, Kwang-Won Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2009; 34(6): 515. CrossRef
The effect of concentration and application time of hydrogen peroxide on the microtensile bond strength of resin restorations to the dentin at different depths
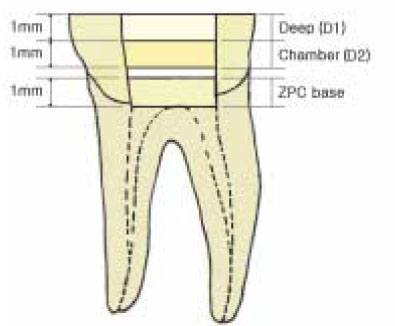
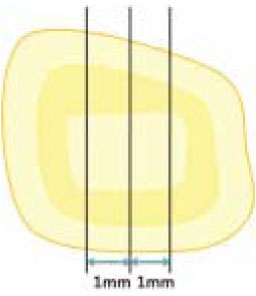
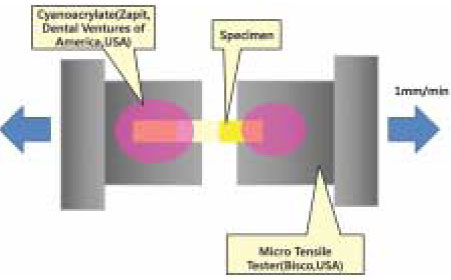
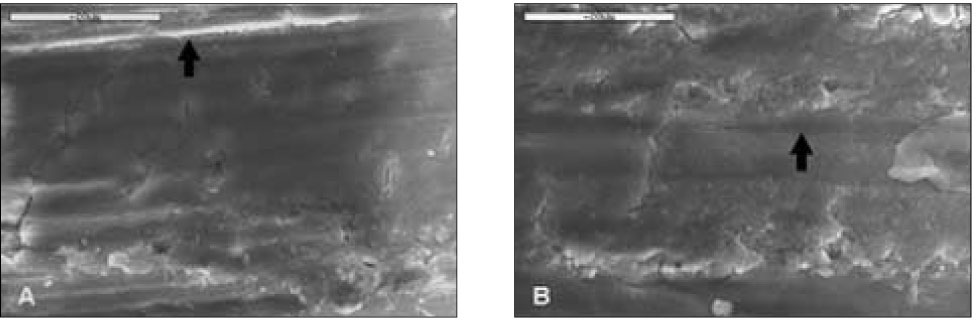
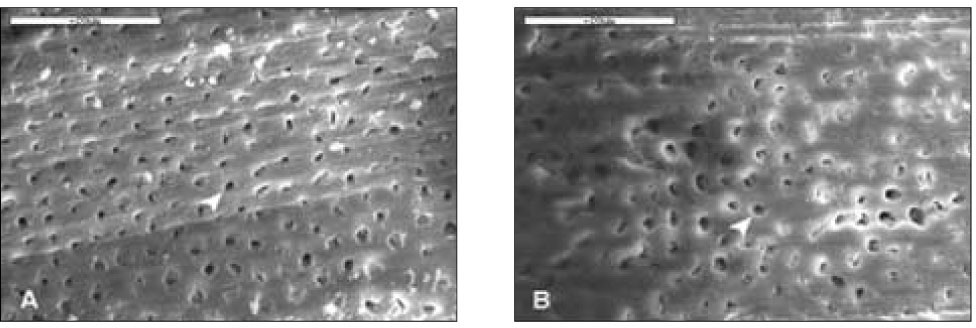
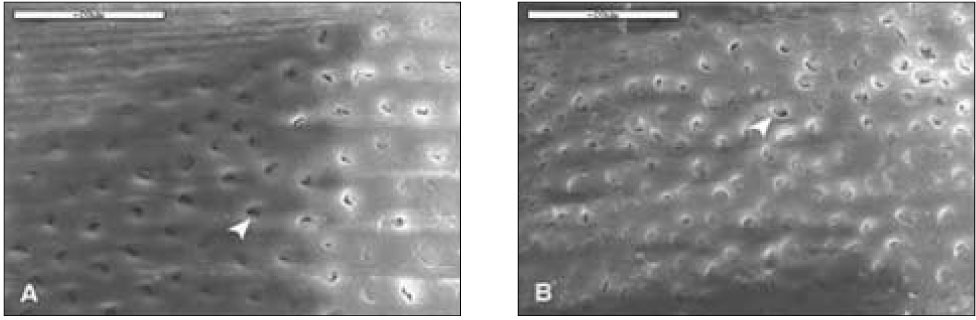
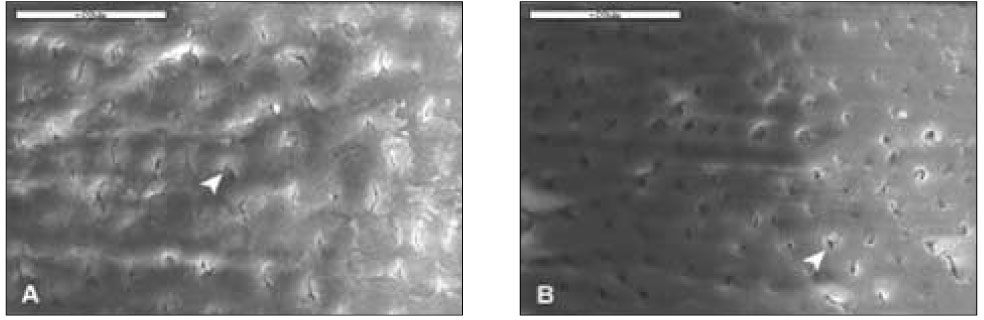
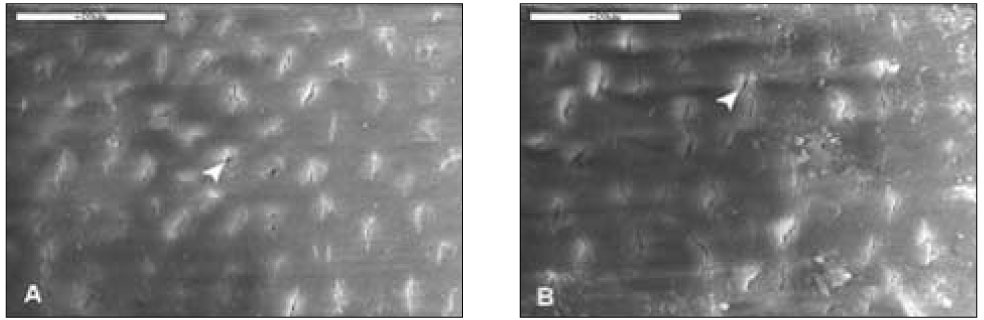
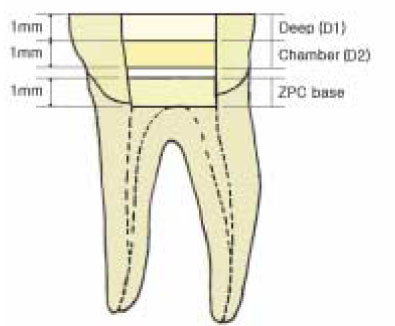
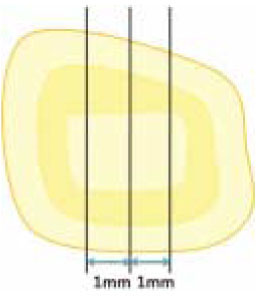
Figure 1
Schematic presentation of the disc preparation at the deep and the pulp chamber dentin
Figure 2
The manufacture of specimen
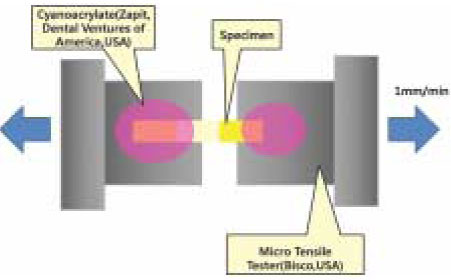
Figure 3
Schematic measurement of the microtensile bond strength
Figure 4
Control group(2K). Most surface was covered with smear layer and had scratches (black arrow) due to using a diamond bur. A. D1, B. D2, Bar=20µm.
Figure 5
With 20% H2O2 for 20min(2K). Dentinal tubules (white arrow head) were opened completely and the smear layer scarcely remained. A. D1, B. D2, Bar=20µm.
Figure 6
With 10% H2O2 for 20min(2K). Dentinal tubules (white arrow head) were opened in a part and the smear layer remained. A. D1, B. D2, Bar=20µm.
Figure 7
With 5% H2O2 for 20min(2K). A. D1, Dentinal tubules (white arrow head) were obscure and covered with the smear layer; B. D2, Dentinal tubules were clear and opened in a part. Bar=20µm.
Figure 8
With 2.5% H2O2 for 20min(2K). Dentinal tubules (white arrow head) were obscure and covered with the smear layer. A: D1; B: D2; the surface of D1 and D2 had a similar pattern; Bar=20µm.
Figure 1
Figure 2
Figure 3
Figure 4
Figure 5
Figure 6
Figure 7
Figure 8
The effect of concentration and application time of hydrogen peroxide on the microtensile bond strength of resin restorations to the dentin at different depths
Averages of the microtensile bond strength to the deep and the pulp chamber dentin by H2O2 concentration and application time(Mean±SD).
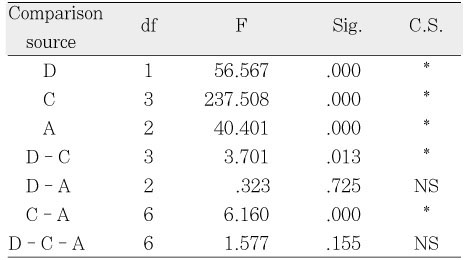
3-way ANOVA results showing the relations among the depth of dentin, the concentration and the application time of H2O2
D: Depth, C: Concentrations, A: Application times
*: significant, NS: not significant
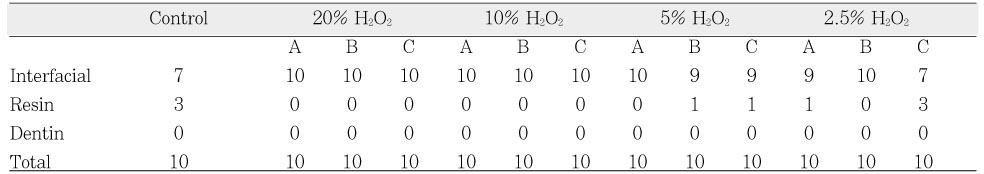
Interfacial, Resin and Dentin failures in D1.
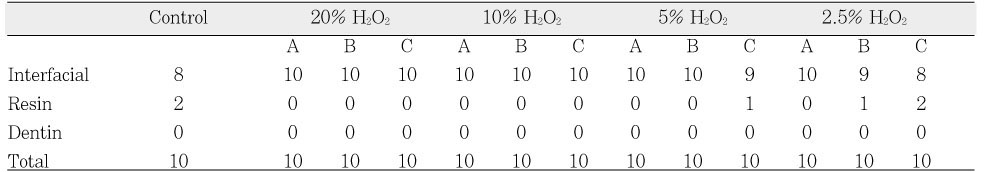
Interfacial, Resin and Dentin failures in D2.
Table 1
Averages of the microtensile bond strength to the deep and the pulp chamber dentin by H2O2 concentration and application time(Mean±SD).
Table 2
3-way ANOVA results showing the relations among the depth of dentin, the concentration and the application time of H2O2
D: Depth, C: Concentrations, A: Application times *: significant, NS: not significant
Table 3
Interfacial, Resin and Dentin failures in D1.
Table 4
Interfacial, Resin and Dentin failures in D2.

 KACD
KACD
 ePub Link
ePub Link Cite
Cite

