Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
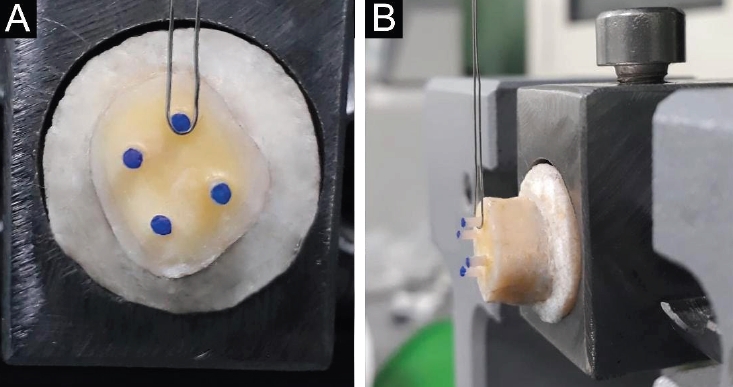
- Bonding and fractographic characterization of universal adhesives applied to dentin in multimode strategies: an in vitro study
- Samaa M. Morsy, Rim Bourgi, Louis Hardan, Carlos Enrique Cuevas-Suárez, Naji Kharouf, Ahmed A. Holiel
- Restor Dent Endod 2026;51(1):e12. Published online February 26, 2026
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2026.51.e12
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Objectives
Universal adhesives (UAs) are marketed as versatile systems for both self-etch (SE) and total-etch (TE) modes. While their bond strength has been widely investigated, evidence linking fracture characteristics to bonding performance remains limited. This study evaluated the micro-shear bond strength (μSBS) and failure patterns of three UAs applied in SE and TE modes, complemented by fractographic scanning electron microscopy (SEM) analysis.
Methods
Eighteen extracted human molars were sectioned to expose mid-coronal dentin and randomly allocated to SE or TE application. Three UAs were tested: Tetric N-Bond Universal, All-Bond Universal, and Single Bond Universal (SBU). Composite micro-rods (n = 72) were bonded, thermocycled for 500 cycles between 5°C and 55°C, and subjected to μSBS testing. Fracture surfaces were examined under SEM and classified as adhesive, cohesive, or mixed. Data were analyzed using two-way analysis of variance, Tukey post hoc test, and Spearman correlation (α = 0.05).
Results
In TE mode, SBU demonstrated the highest μSBS (p < 0.001), whereas no significant differences were observed among adhesives in SE mode (p > 0.05). SEM analysis revealed adhesive failures as interfacial fractures, cohesive failures with beach marks, and mixed failures involving crack propagation through both dentin and composite. Adhesive failures correlated negatively with μSBS (rs = –0.77), while mixed failures correlated positively (rs = 0.81).
Conclusions
Both the etching strategy and adhesive formulation significantly affect bond strength and fracture behavior. Fractographic SEM analysis provides critical insights into the mechanical reliability of UAs and informs their clinical application.
- 215 View
- 24 Download

- Effect of chlorhexidine application on the bond strength of resin core to axial dentin in endodontic cavity
- Yun-Hee Kim, Dong-Hoon Shin
- Restor Dent Endod 2012;37(4):207-214. Published online November 21, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2012.37.4.207
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study evaluated the influence of chlorhexidine (CHX) on the microtensile bonds strength (µTBS) of resin core with two adhesive systems to dentin in endodontic cavities.
Materials and Methods Flat dentinal surfaces in 40 molar endodontic cavities were treated with self-etch adhesive system, Contax (DMG) and total-etch adhesive system, Adper Single Bond 2 (3M ESPE) after the following surface treatments: (1) Priming only (Contax), (2) CHX for 15 sec + rinsing + priming (Contax), (3) Etching with priming (Adper Single Bond 2), (4) Etching + CHX for 15 sec + rinsing + priming (Adper Single Bond 2). Resin composite build-ups were made with LuxaCore (DMG) using a bulk method and polymerized for 40 sec. For each condition, half of specimens were submitted to µTBS after 24 hr storage and half of them were submitted to thermocycling of 10,000 cycles between 5℃ and 55℃ before testing. The data were analyzed using ANOVA and independent
t -test at a significance level of 95%.Results CHX pre-treatment did not affect the bond strength of specimens tested at the immediate testing period, regardless of dentin surface treatments. However, after 10,000 thermocycling, all groups showed reduced bond strength. The amount of reduction was greater in groups without CHX treatments than groups with CHX treatment. These characteristics were the same in both self-etch adhesive system and total-etch adhesive system.
Conclusions 2% CHX application for 15 sec proved to alleviate the decrease of bond strength of dentin bonding systems. No significant difference was shown in µTBS between total-etching system and self-etching system.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Micro Tensile bond strength and microleakage assessment of total-etch and self-etch adhesive bonded to carious affected dentin disinfected with Chlorhexidine, Curcumin, and Malachite green
Zeeshan Qamar, Nishath Sayed Abdul, R Naveen Reddy, Mahesh Shenoy, Saleh Alghufaili, Yousef Alqublan, Ali Barakat
Photodiagnosis and Photodynamic Therapy.2023; 43: 103636. CrossRef - The Classification and Selection of Adhesive Agents; an Overview for the General Dentist
Naji Ziad Arandi
Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dentistry.2023; Volume 15: 165. CrossRef - Influence of chlorhexidine 2% and sodium hypochlorite 5.25% on micro-tensile bond strength of universal adhesive system (G-Premio Bond)
Nafiseh Fazelian, Abbas Rahimi Dashtaki, MohammadAmin Eftekharian, Batool Amiri
Brazilian Journal of Oral Sciences.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of the effects of different methods of post space preparation in primary anterior teeth on the fracture resistance of tooth restorations
Bahman Seraj, Sara Ghadimi, Ebrahim Najafpoor, Fatemeh Abdolalian, razieh khanmohammadi
Journal of Dental Research, Dental Clinics, Dental Prospects.2019; 13(2): 141. CrossRef - Chemical, microbial, and host‐related factors: effects on the integrity of dentin and the dentin–biomaterial interface
Marcela T. Carrilho, Fabiana Piveta, Leo Tjäderhane
Endodontic Topics.2015; 33(1): 50. CrossRef - MMP Inhibitors on Dentin Stability
A.F. Montagner, R. Sarkis-Onofre, T. Pereira-Cenci, M.S. Cenci
Journal of Dental Research.2014; 93(8): 733. CrossRef - Thermal cycling for restorative materials: Does a standardized protocol exist in laboratory testing? A literature review
Anna Lucia Morresi, Maurizio D'Amario, Mario Capogreco, Roberto Gatto, Giuseppe Marzo, Camillo D'Arcangelo, Annalisa Monaco
Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials.2014; 29: 295. CrossRef
- Micro Tensile bond strength and microleakage assessment of total-etch and self-etch adhesive bonded to carious affected dentin disinfected with Chlorhexidine, Curcumin, and Malachite green
- 1,406 View
- 3 Download
- 7 Crossref

- The effects of total-etch, wet-bonding, and light-curing of adhesive on the apical seal of a resin-based root canal filling system
- Won-Il Ryu, Won-Jun Shon, Seung-Ho Baek, In-Han Lee, Byeong-Hoon Cho
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2011;36(5):385-396. Published online September 30, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2011.36.5.385
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study evaluated the effects of adhesion variables such as the priming concepts of canal wall and the curing modes of adhesives on the sealing ability of a resin-based root canal filling system.
Materials and Methods Apical microleakage of the Resilon-RealSeal systems filled with 3 different combinations of adhesion variables was compared with the conventional gutta-percha filling using a dye penetration method. Experimental groups were SEDC, Resilon (Resilon Research LLC) filling with self-etch RealSeal (SybronEndo) primer and dual-cure RealSeal sealer; NELC, Resilon filling with no etching, Scotchbond Multi-Purpose (3M ESPE) primer application and light-curing adhesive; and TELC, Resilon filling with Scotchbond Multi-Purpose primer and adhesive used under total etch / wet bonding and light-cure protocols. GPCS, gutta-percha filling with conventional AH26 plus sealer, was the control group.
Results The median longitudinal dye penetration length of TELC was significantly shorter than those of GPCS and SEDC (Kruskal-Wallis test,
p < 0.05). In the cross-sectional microleakage scores, TELC showed significant differences from other groups at 2 to 5 mm from the apical foramen (Kruskal-Wallis test,p < 0.05).Conclusions When a resin-based root canal filling material was used, compared to the self-etching primer and the dual-cure sealer, the total etch/wet-bonding with primer and light-curing of adhesive showed improved apical sealing and was highly recommended.
- 1,303 View
- 1 Download

- The effect of Er,Cr:YSGG irradiation on microtensile bond strength of composite resin restoration
- Jeong-Hye Son, Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Bock Hur, Jeong-Kil Park
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2010;35(2):134-142. Published online March 31, 2010
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2010.35.2.134
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purpose of this study was to evaluate the effect of Er,Cr:YSGG laser irradiation with hypersensitivity mode on microtensile bond strength of composite resin. Twenty extracted permanent molars were randomly assigned to six groups, according to the irradiation of Er,Cr:YSGG laser, adhesive system (Optibond FL or Clearfil SE bond) and application time of etchant (15 sec or 20 sec). Then composite resin was build up on each conditioned surface. The restored teeth were stored in distilled water at room temperature for 24 h and twelve specimens for each group were prepared. All specimens were subjected to microtensile bond strength and the fracture modes were evaluated. Also, the prepared dentin surface and laser irradiated dentin surface were examined under SEM.
The results were as follows:
The microtensile bond strength of laser irradiated group was lower than that of no laser irradiated group.
Regardless of laser irradiation, the microtensile bond strength of Optibond FL was higher than that of Clearfil SE bond. And the microtensile bond strength of 20 sec etching group was higher than that of 15 sec etching group when using Optibond FL.
The SEM image of laser irradiated dentin surface showed prominent peritubular dentin, opened dentinal tubules and no smear layer.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Enamel pretreatment with Er:YAG laser: effects on the microleakage of fissure sealant in fluorosed teeth
Mahtab Memarpour, Nasrin Kianimanesh, Bahareh Shayeghi
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2014; 39(3): 180. CrossRef
- Enamel pretreatment with Er:YAG laser: effects on the microleakage of fissure sealant in fluorosed teeth
- 1,539 View
- 5 Download
- 1 Crossref

- The bonding durability of total etching adhesives on dentin
- Mi-Ra Jung, Gi-Woon Choi, Sang-Hyuk Park, Sang-Jin Park
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2007;32(4):365-376. Published online July 31, 2007
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2007.32.4.365
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purpose of this study was to evaluate the effect of different etching times on microtensile bond strength (µTBS) to dentin both initial and after thermocycling with 3 different types of total-etching adhesives.
Fifty four teeth were divided into 18 groups by etching times (5, 15, 25 sec), adhesives types (Scotchbond Multipurpose (SM), Single Bond (SB), One-Step (OS)), and number of thermocycling (0, 2,000 cycles).
Flat dentin surfaces were prepared on mid-coronal dentin of extracted third molars. After exposed fresh dentin surfaces were polished with 600-grit SiC papers, each specimen was acid-etched with 35% phosphoric acid (5, 15, 25 sec) and bonded with 3 different types of total etching adhesives respectively. Then, hybrid composite Z-250 was built up. Half of them were not thermocycled (control group) and the others were subjected to 2,000 thermocycle (experimental group). They were sectioned occluso-gingivally into 1.0 × 1.0 mm2 composite-dentin beams and tested with universal testing machine at a crosshead speed of 1.0 mm/min.
Within limited data of this study, the results were as follows
1. There was no statistically significant difference in µTBS between the thermocycled and non-thermocycled groups, except for both SM and SB etched for 25 sec.
2. In thermocycled SM and SB groups, bond strength decreased by extended etching time.
In total etching systems, adhesive durability for dentin could be affected by type of solvents in adhesive and etching time. Especially, extended etching time may cause deteriorate effects on bond strength when ethanol-based adhesive was used.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Difference in bond strength according to filling techniques and cavity walls in box-type occlusal composite resin restoration
Eun-Joo Ko, Dong-Hoon Shin
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2009; 34(4): 350. CrossRef
- Difference in bond strength according to filling techniques and cavity walls in box-type occlusal composite resin restoration
- 1,225 View
- 6 Download
- 1 Crossref

- THE EFFECT OF THERMOCYCLING ON THE DURABILITY OF DENTIN ADHESIVE SYSTEMS
- Young-Hoon Moon, Jong-Ryul Kim, Kyung-Kyu Choi, Sang-Jin Park
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2007;32(3):222-235. Published online January 14, 2007
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2007.32.3.222
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Abstract The objectives of this study was to evaluate the effect of thermocycling on the μTBS (microtensile bond strength) to dentin with four different adhesive systems to examine the bonding durability.
Freshly extracted 3rd molar teeth were exposed occlusal dentin surfaces, and randomly distributed into 8 adhesive groups: 3-steps total-etching (Scotchbond Multi-Purpose Plus; SM, All Bond-2; AB), 2-steps total-etching (Single Bond; SB, One Step plus; OS), 2-steps self-etching (Clearfil SE Bond; SE, AdheSE; AD) and single-step self-etching systems (Promp L-Pop; PL, Xeno III; XE). Each adhesive system in 8 adhesives groups was applied on prepared dentin surface as an instruction and resin composite (Z250) was placed incrementally and light-cured. The bonded specimens were sectioned with low-speed diamond saw to obtain 1 × 1 ㎜ sticks after 24 hours of storage at 37 °C distilled water and proceeded thermocycling at the pre-determined cycles of 0, 1,000 and 2,000. The μTBS test was carried out with EZ-tester at 1 mm/min. The results of bond strength test were statistically analyzed using one-way ANOVA/ Duncan's test at the α〈 0.05 confidence level. Also, the fracture mode of debonded surface and the interface were examined under SEM.
The results of this study were as follows;
3-step total etching adhesives showed stable, but bond strength of 2-step adhesives were decreased as thermocycling stress.
SE showed the highest bond strength, but single step adhesives (PL, XE) had the lowest value both before and after thermocycling.
Most of adhesives showed adhesive failure. The total-etching systems were prone to adhesive failure and the single-step systems were mixed failure after thermocycling.
Within limited results of this study, the bond strength of adhesive system was material specific and the bonding durability was affected by the bonding step/ procedure of adhesive. Simplified bonding procedures do not necessarily imply improved bonding performance.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Physical characterization and bond performance of a non-methacrylate dental adhesive in long-term biochemical and thermal aging models
Zach Gouveia, Rastin Rahiminejad, Lingyun Zhu, Jesse Barker, Yoav Finer, J. Paul Santerre
Dental Materials.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of Er:YAG lasing on the dentin bonding strength of two-step adhesives
Byeong-Choon Song, Young-Gon Cho, Myung-Seon Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2011; 36(5): 409. CrossRef - Quantitative comparison of permeability in the adhesive interface of four adhesive systems
Juhea Chang, Keewook Yi, Hae-Young Kim, In Bog Lee, Byeong Hoon Cho, Ho-Hyun Son
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2009; 34(1): 51. CrossRef
- Physical characterization and bond performance of a non-methacrylate dental adhesive in long-term biochemical and thermal aging models
- 1,828 View
- 13 Download
- 3 Crossref


 KACD
KACD

 First
First Prev
Prev


