Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Surgical management of maxillary sinusitis of endodontic origin after reestablishing maxillary sinus floor healing through a nonsurgical approach: a case report
- Eun-Sook Kang, Min-Kyeong Kim, Mi-Kyung Yu, Kyung-San Min
- Restor Dent Endod 2025;50(2):e12. Published online April 8, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2025.50.e12
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
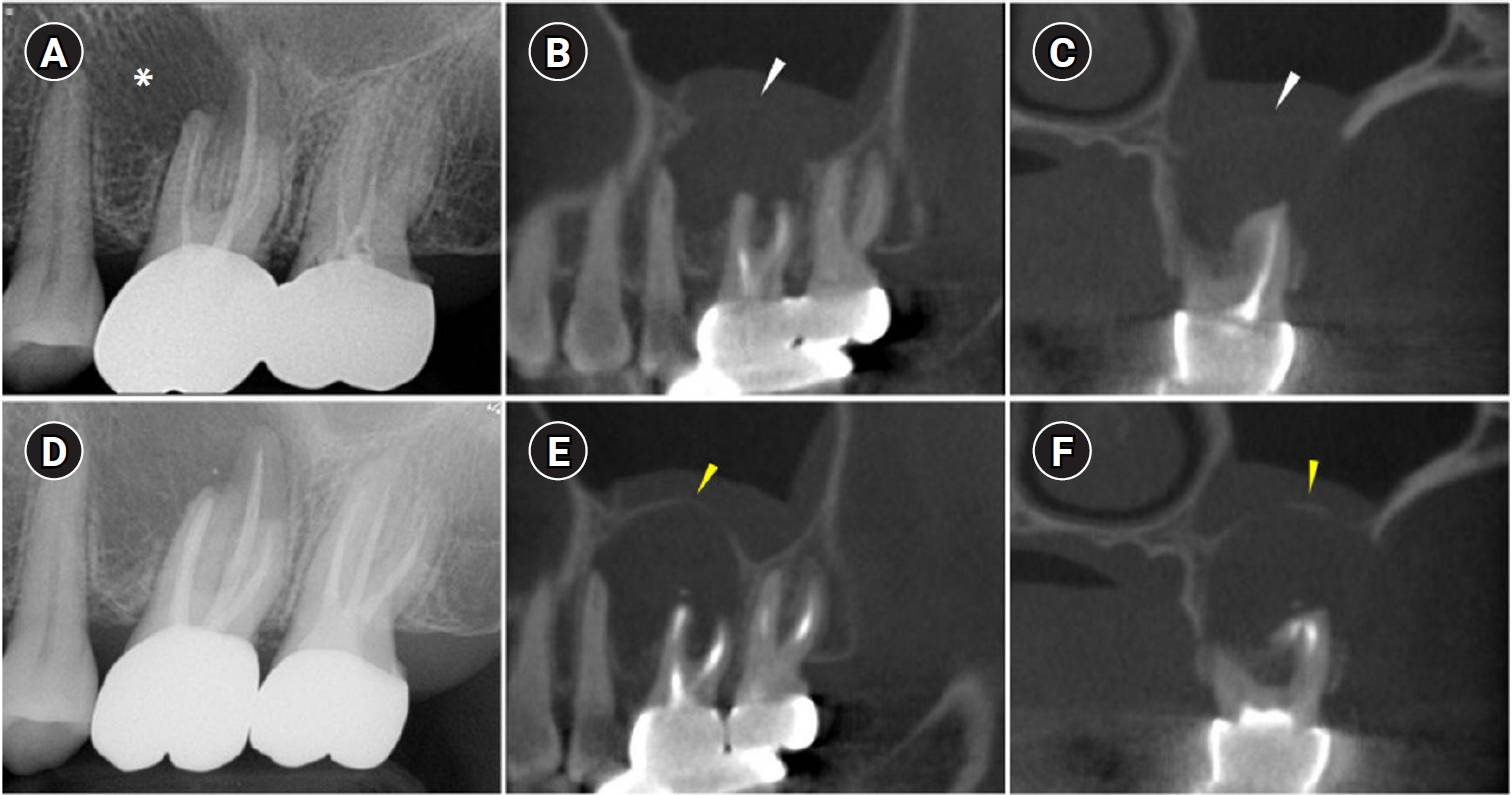
ePub - When root canal infections breach the maxillary sinus floor (MSF), maxillary sinusitis of endodontic origin (MSEO) can result. This case illustrates the surgical management of MSEO following the nonsurgical reestablishment of the MSF. A 55-year-old woman presented with left facial pain and was diagnosed with MSEO originating from the left upper first molar. Despite undergoing nonsurgical root canal treatment, there was no evidence of bony healing after 6 months. However, cone-beam computed tomographic (CBCT) scans revealed the reestablishment of MSF. Subsequently, surgical intervention was carried out using a dental operating microscope. Two years after surgery, CBCT images indicated that the mucosal edema had resolved, and the MSF was well reestablished. Preserving the MSF is crucial for the success of endodontic surgery. When MSEO is present, the integrity of the MSF must be assessed to determine appropriate treatment options.
- 4,091 View
- 208 Download

- Proximity of maxillary molar apexes to the cortical bone surface and the maxillary sinus
- Han Shin Lee, Dokyung Kim, Sung Kyo Kim
- Restor Dent Endod 2022;47(3):e33. Published online August 8, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2022.47.e33
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study aimed to analyze the proximity of maxillary molar roots to their overlying cortical bone surfaces and the maxillary sinus.
Materials and Methods Cone-beam computed tomographic images of 151 patients with completely erupted upper molars that had 3 separate roots were studied. The following distances were measured: from the root apex to the cortical plate and maxillary sinus floor, and from the apical 3-mm level of the root to the cortical plate. Differences between groups were analyzed with 1-way analysis of variance and the Scheffé
post hoc test, the significance of differences between cone-beam computed tomography views with the pairedt -test, and the significance of differences among age groups with linear regression analysis. The significance level was set atp < 0.05.Results The mesiobuccal and distobuccal root apexes of maxillary second molars were more distant from the buccal cortical plate than the maxillary first molars (
p < 0.05). The apical 3-mm level of the mesiobuccal root of the first molar was closer to the buccal cortical bone than the second molar (p < 0.05). In the maxillary first molars, the thickness of the buccal cortical bone decreased in all roots with age (p < 0.05). In all root apexes of both molars, the difference in the vertical level between the maxillary sinus floor and the root apex increased with age (p < 0.05).Conclusions Awareness of the anatomical profile of maxillary molar apices in relation to the cortical bones and maxillary sinus will be beneficial for apical surgery.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Proximity of maxillary molar palatal roots to adjacent structures for endodontic microsurgery: a cone-beam computed tomography study
Xiaoxiang Huang, Jun Xu, Benxiang Hou, Ying Wang
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Periapical bone loss configuration in sub-Saudi patients afflicted with periapical abscesses: A 3D cone-beam computed tomography analysis
Swati A. Srivastava, Rahaf A. Alawajy, Rehab Abdelaziz, Elzahraa A. Eldwakhly, Selma A. Saadaldin, Rahaf A. Almohareb, Fahda Nabeel Algahtani, Mai Salah Soliman, Manal M. Abdelhafeez
Saudi Endodontic Journal.2025; 15(2): 144. CrossRef
- Proximity of maxillary molar palatal roots to adjacent structures for endodontic microsurgery: a cone-beam computed tomography study
- 3,253 View
- 29 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref

- Chronic maxillary sinusitis caused by root canal overfilling of Calcipex II
- Jin-Woo Kim, Kyung-Mo Cho, Se-Hee Park, Soh-Ra Park, Sang-Shin Lee, Suk-Keun Lee
- Restor Dent Endod 2014;39(1):63-67. Published online January 20, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2014.39.1.63
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub This is a case report of chronic maxillary sinusitis caused by root canal overfilling of Calcipex II (Techno-Dent). A 60 year-old male complained of dull pain in the right maxillary molar area after complicated endodontic treatment using Calcipex II paste and was finally diagnosed with a chronic maxillary sinusitis through a clinical and radiological observation. In the biopsy examination, the periapical granuloma contained a lot of dark and translucent Calcipex II granules which were not stained with hematoxylin and eosin. They were usually engulfed by macrophages but rarely resorbed, resulting in scattering and migrating into antral mucosa. Most of the Calcipex II granules were also accumulated in the cytoplasms of secretory columnar epithelial cells, and small amount of Calcipex II granules were gradually secreted into sinus lumen by exocytosis. However, chronic granulomatous inflammation occurred without the additional recruitment of polymorphonuclear leukocytes (PMNs) and lymphocytes, and many macrophages which engulfed the Calcipex II granules were finally destroyed in the processes of cellular apoptosis. It is presumed that Calcipex II granules are likely to have a causative role to induce the granulomatous foreign body inflammation in the periapical region, and subsequently to exacerbate the chronic maxillary sinusitis in this study.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Removal of Calcium Hydroxide Paste Leaked Into the Maxillary Sinus
Dohee Kim, Young Kim, Jeong Joon Han
Ear, Nose & Throat Journal.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Synergistic effects of reduced graphene oxide on the antibacterial activity of calcium hydroxide-based intracanal medicaments containing different vehicles
Mi-Ah Kim, Min-Kyeong Kim, Eun-Sook Kang, Kyung-San Min
Journal of Oral Science.2025; 67(1): 35. CrossRef - The effect of extrusion of the filling material on the periapical status
M. Yu. Pokrovsky, T. P. Goryacheva, A. М. Pokrovskiy, O. А. Aleshina
Endodontics Today.2025; 23(1): 31. CrossRef - Rheological properties and handling characteristics of four injectable calcium hydroxide pastes
Min-Jung KIM, In-Bog LEE
Dental Materials Journal.2024; 43(6): 796. CrossRef - Assessing the efficacy of jet dispenser versus direct syringe injection for calcium hydroxide paste placement in artificial root canals
Youngwook Song, Hwichan Ham, WooCheol Lee, Ryan Jin Young Kim
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - A white cloud in the antrum: Maxillary sinusitis following an endodontic treatment
Kamis Gaballah, Mawada Hassan
Asian Journal of Surgery.2023; 46(4): 1690. CrossRef - Electronic Apex Locators and their Implications in Contemporary Clinical Practice: A Review
Zainab Shirazi, Anas Al-Jadaa, Abdul Rahman Saleh
The Open Dentistry Journal.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The significance of diagnosis and treatment planning in periapical lesion overfilled with calcium hydroxide paste
Kyoung-Hwa Jung, Eun-Young Kwon, Youn-Kyung Choi, So-Yeun Kim, Hye-Mi Jeon, Jeong-Kil Park
Journal of Dental Rehabilitation and Applied Science.2021; 37(2): 95. CrossRef - Maxillary antroliths detected by cone-beam computed tomography in an adult dental population
Bong-Hae Cho, Yun-Hoa Jung, Jae-Joon Hwang
Imaging Science in Dentistry.2019; 49(1): 59. CrossRef - Influence of the Maxillary Sinus on the Accuracy of the Root ZX Apex Locator: An Ex Vivo Study
Roula El Hachem, Elie Wassef, Nadim Mokbel, Richard Abboud, Carla Zogheib, Nada El Osta, Alfred Naaman
Dentistry Journal.2019; 7(1): 3. CrossRef - Removal efficacy and cytotoxicity of a calcium hydroxide paste using N-2-methyl-pyrrolidone as a vehicle
Myung-Jin Lim, Hyun-Jin Jang, Mi-Kyung Yu, Kwang-Won Lee, Kyung-San Min
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2017; 42(4): 290. CrossRef - A case of high density abnormality in x-ray findings of mandible caused by leakage of root canal filling paste
Haruko Kashiwamura, Kyoko Oka, Yoko Tuchihashi, Hanako Yoshioka, Mayumi Kato, Atsuko Baba, Toyohiro Kagawa, Kazuhiko Okamura, Masao Ozaki
Pediatric Dental Journal.2017; 27(3): 162. CrossRef - Maxillary Sinus Impaction of a Core Carrier Causing Sustained Apical Periodontitis, Sinusitis, and Nasal Stenosis: A 3-year Follow-up
Lars Bjørndal, Catharina Amaloo, Merete Markvart, Vibe Rud, Klaus Qvortrup, Camilla Stavnsbjerg, Thomas Bjarnsholt
Journal of Endodontics.2016; 42(12): 1851. CrossRef - Proximity of Posterior Teeth to the Maxillary Sinus and Buccal Bone Thickness: A Biometric Assessment Using Cone-beam Computed Tomography
Sung Hyun Kang, Bom Sahn Kim, Yemi Kim
Journal of Endodontics.2015; 41(11): 1839. CrossRef
- Removal of Calcium Hydroxide Paste Leaked Into the Maxillary Sinus
- 2,273 View
- 8 Download
- 14 Crossref


 KACD
KACD

 First
First Prev
Prev


