Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Analysis of the reciprocating kinematics of the VDW Silver Reciproc, E-Connect Pro, Ecom, and Endopen endodontic motors: an in vitro experimental study
- Cristielly França, Juliana D. Bronzato, Dieimes Braambati, Adriana de-Jesus-Soares, Carla C. R. B. Félix, Michelle A. N. S. Ferreira, Marcos Frozoni
- Restor Dent Endod 2026;51(1):e5. Published online January 20, 2026
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2026.51.e5

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Objectives
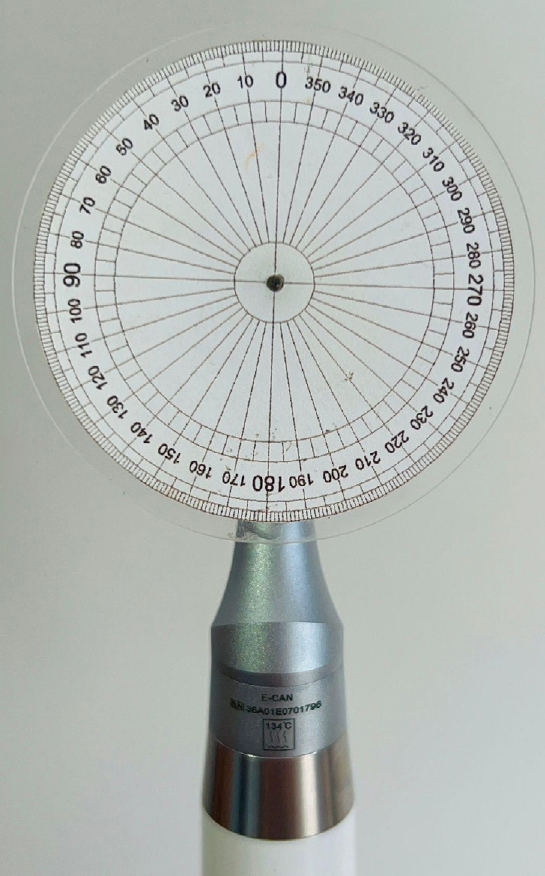
This study aimed to evaluate the actual parameters of four endodontic motors, each adjusted for reciprocating motion, and compare them to the manufacturers’ declared values.
Methods
The motors used were the VDW Silver Reciproc (VDW GmbH), E-Connect Pro (MK Life), Ecom (Woodpecker), and Endopen (Schuster Woodpecker). A custom optical target was attached to the motor contra-angle, the movements were recorded with a high-resolution camera, and the images were analyzed. Engagement, disengagement, net angles, and speed for each operation cycle, duration of clockwise (CW) and counter-clockwise (CCW) movement, duration of standstill after CW and CCW movement, and the number of cycles to complete a full rotation were analyzed. The data were statistically analyzed at a significance level of 5%. The replicability of all reciprocal parameters analyzed was statistically different from that reported by the manufacturers.
Results
There was no statistically significant difference between the VDW Silver Reciproc, Ecom, and Endopen for the engagement angle. The E-Connect Pro was the least reliable at the 150°/30° settings for both angle parameters. There was no significant difference between the set and actual cycle net angles for the VDW Silver Reciproc (p = 0.493). While the actual values for the Ecom and E-Connect Pro were significantly higher than the set (p < 0.001), the actual values for the Endopen were significantly lower than the set (p < 0.001).
Conclusions
Experiments on four commercially available reciprocating endodontic motors revealed that the actual motor values differed significantly from the set values.
- 583 View
- 27 Download

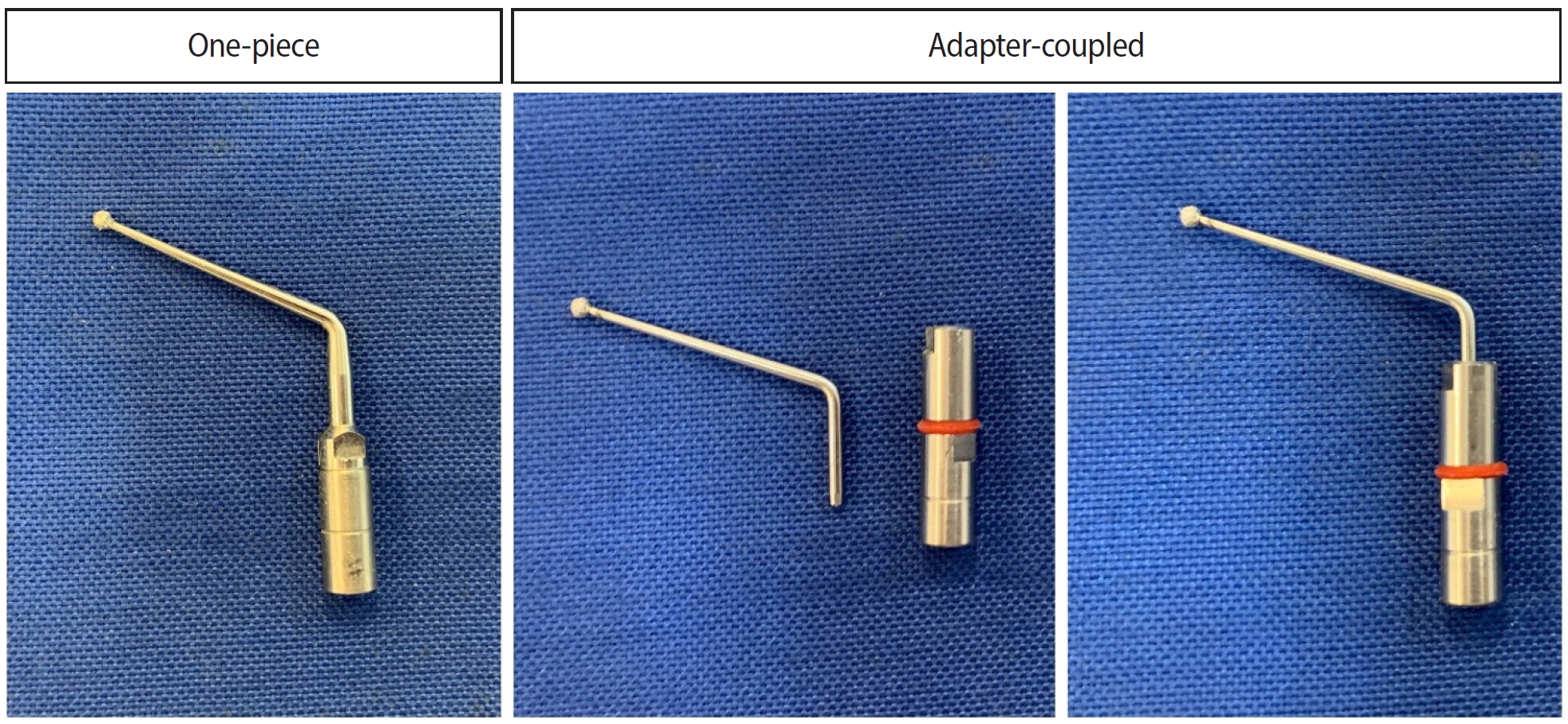
- Analysis of thermal profiles on tooth structure and insert during one-piece or adapter-coupled ultrasonic insert use: an in vitro experimental study
- Gabriela Loewen Brotto, Bruno Monguilhott Crozeta, Bruno Marques-da-Silva, Alysson Nunes Diógenes, Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal da Silva, Flávia Sens Fagundes Tomazinho
- Restor Dent Endod 2025;50(3):e24. Published online July 11, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2025.50.e24
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Objectives
This in vitro study aimed to evaluate temperature variation on the external surface of mandibular molars and within ultrasonic inserts when using adapter-coupled versus one-piece inserts.
Methods
Twenty-four extracted human mandibular molars were divided into two groups based on the type of ultrasonic insert used: adapter-coupled and one-piece inserts. Temperature on the external surface of each tooth was measured with a thermocouple probe positioned in the furcation area, capturing data continuously. The temperature of the ultrasonic inserts was monitored in real-time using a thermal imaging camera. Measurements were taken in a controlled environment without cooling for over 120 seconds. Statistical analysis was conducted using analysis of variance (ANOVA) and two-way ANOVA with repeated measures to evaluate temperature variations between groups and over time, with significance set at 5%.
Results
In the external tooth surface temperature measurements, no significant differences were observed between the groups during the initial 15 seconds (p = 0.185) and 30 seconds (p = 0.067). However, significant differences emerged at 60 seconds (p = 0.025), 90 seconds (p = 0.024), and 120 seconds (p = 0.020), with the one-piece insert group demonstrating higher temperatures in the furcation region. Thermal imaging of the inserts revealed a significant difference at all time points (p < 0.001), with adapter-coupled inserts showing greater heating.
Conclusions
The use of ultrasonic inserts leads to a gradual rise in temperature on the external tooth surface. One-piece inserts generated higher temperatures on the tooth, while adapter-coupled inserts exhibited greater heating within the insert.
- 1,811 View
- 95 Download

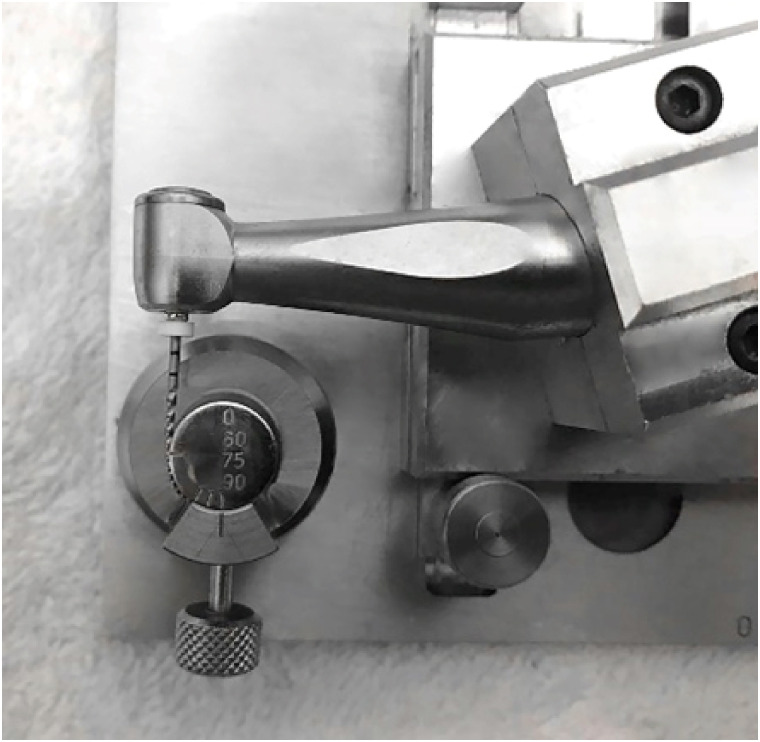
- Comparative analysis of torsional and cyclic fatigue resistance of ProGlider, WaveOne Gold Glider, and TruNatomy Glider in simulated curved canal
- Pedro de Souza Dias, Augusto Shoji Kato, Carlos Eduardo da Silveira Bueno, Rodrigo Ricci Vivan, Marco Antonio Hungaro Duarte, Pedro Henrique Souza Calefi, Rina Andréa Pelegrine
- Restor Dent Endod 2023;48(1):e4. Published online December 8, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2023.48.e4
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study aimed to compare the torsional and cyclic fatigue resistance of ProGlider (PG), WaveOne Gold Glider (WGG), and TruNatomy Glider (TNG).
Materials and Methods A total of 15 instruments of each glide path system (
n = 15) were used for each test. A custom-made device simulating an angle of 90° and a radius of 5 millimeters was used to assess cyclic fatigue resistance, with calculation of number of cycles to failure. Torsional fatigue resistance was assessed by maximum torque and angle of rotation. Fractured instruments were examined by scanning electron microscopy (SEM). Data were analyzed with Shapiro-Wilk and Kruskal-Wallis tests, and the significance level was set at 5%.Results The WGG group showed greater cyclic fatigue resistance than the PG and TNG groups (
p < 0.05). In the torsional fatigue test, the TNG group showed a higher angle of rotation, followed by the PG and WGG groups (p < 0.05). The TNG group was superior to the PG group in torsional resistance (p < 0.05). SEM analysis revealed ductile morphology, typical of the 2 fracture modes: cyclic fatigue and torsional fatigue.Conclusions Reciprocating WGG instruments showed greater cyclic fatigue resistance, while TNG instruments were better in torsional fatigue resistance. The significance of these findings lies in the identification of the instruments’ clinical applicability to guide the choice of the most appropriate instrument and enable the clinician to provide a more predictable glide path preparation.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Buckling resistance of various pathfinding endodontic instruments: An in vitro study
Ujjwal Das, Rajesh Kumar Das, Kallol Kumar Saha, Lugu Buru Murmu, Srimanta Banerjee, Rishila Nag
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2025; 28(4): 384. CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of the remaining dentin volume following instrumentation with rotary, reciprocating, and hand files during root canal treatment in primary molars: An ex vivo study
İrem Eren, Berkant Sezer
Journal of Dental Sciences.2024; 19(4): 2126. CrossRef - Screw-in force, torque generation, and performance of glide-path files with three rotation kinetics
Jee-Yeon Woo, Ji-Hyun Jang, Seok Woo Chang, Soram Oh
Odontology.2024; 112(3): 761. CrossRef - Evaluation of shaping ability of different glide path instruments: a micro-computed tomography study
Merve Yeniçeri Özata, Seda Falakaloğlu, Ali Keleş, Özkan Adıgüzel, Mustafa Gündoğar
BMC Oral Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef
- Buckling resistance of various pathfinding endodontic instruments: An in vitro study
- 2,906 View
- 68 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref

-
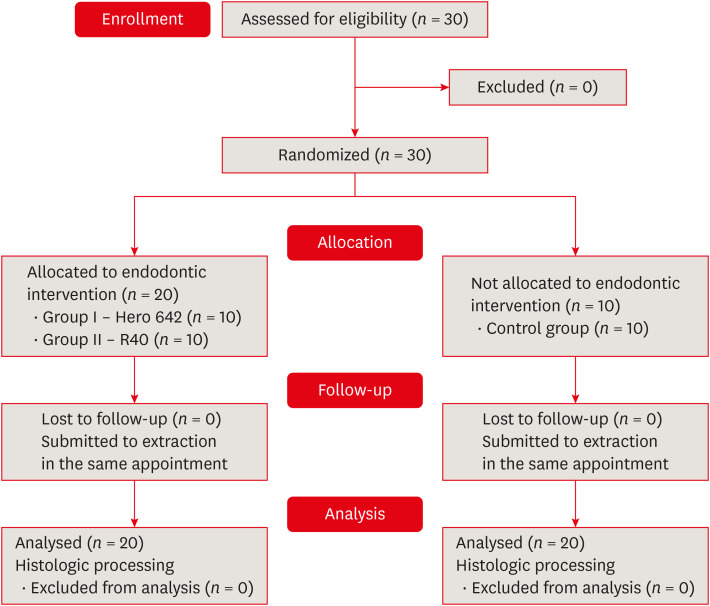
Apical root canal cleaning after preparation with endodontic instruments: a randomized trial
in vivo analysis - Volmir João Fornari, Mateus Silveira Martins Hartmann, José Roberto Vanni, Rubens Rodriguez, Marina Canali Langaro, Lauter Eston Pelepenko, Alexandre Augusto Zaia
- Restor Dent Endod 2020;45(3):e38. Published online June 24, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2020.45.e38
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study aimed to evaluate vital pulp tissue removal from different endodontic instrumentation systems from root canal apical third
in vivo .Materials and Methods Thirty mandibular molars were selected and randomly divided into 2 test groups and one control group. Inclusion criteria were a positive response to cold sensibility test, curvature angle between 10 and 20 degrees, and curvature radius lower than 10 mm. Root canals prepared with Hero 642 system (size 45/0.02) (
n = 10) and Reciproc R40 (size 40/0.06) (n = 10) and control (n = 10) without instrumentation. Canals were irrigated only with saline solution during root canal preparation. The apical third was evaluated considering the touched/untouched perimeter and area to evaluate the efficacy of root canal wall debridement. Statistical analysis usedt -test for comparisons.Results Untouched root canal at cross-section perimeter, the Hero 642 system showed 41.44% ± 5.62% and Reciproc R40 58.67% ± 12.39% without contact with instruments. Regarding the untouched area, Hero 642 system showed 22.78% ± 6.42% and Reciproc R40 34.35% ± 8.52%. Neither instrument achieved complete cross-sectional root canal debridement. Hero 642 system rotary taper 0.02 instruments achieved significant greater wall contact perimeter and area compared to reciprocate the Reciproc R40 taper 0.06 instrument.
Conclusions Hero 642 achieved higher wall contact perimeter and area but, regardless of instrument size and taper, vital pulp during
in vivo instrumentation is not entirely removed.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Unveiling the correlation between in vivo endodontic reciprocate instrumentation and crack formation
Mateus Silveira Martins Hartmann, José Roberto Vanni, Karla Rovaris, Lucas Jeziorski Hartmann, Lauter Eston Pelepenko, Adriana de-Jesus-Soares, Volmir João Fornari
Journal of Dentistry.2024; 150: 105367. CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of stress distribution against the root canal wall at three different levels using novel NiTi rotary files – A finite element analysis
Rimjhim Singh, Sandeep Dubey, Palak Singh, Praveen Singh Samant, Suparna Ganguly Saha
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2024; 27(1): 62. CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of Ultrasonic and Sonic Irrigant Activation Systems: Assessing Extrusion Risk, Debridement, and Biofilm Removal in Distinct Apical Preparation Sizes
Sara Paixão, Pedro Sousa Gomes, Maria Helena Fernandes, Cláudia Rodrigues, Liliana Grenho
Applied Sciences.2024; 14(9): 3904. CrossRef - A Short Report on the Effectiveness of Edge Taper Platinum and XP-3D Shaper for the Reduction of Enterococcus faecalis Count in the Root Canal System: An Ex Vivo Study
Hanie Moaveni, Parastou Ghahari, Samira Behrad, Majid Mirmohammadkhani, Sobhan Rashmee, Somayeh Teimoori
Avicenna Journal of Dental Research.2024; 16(2): 77. CrossRef - Comparative in Vitro Study on the Antimicrobial Efficacy of Endodontic Sealers Against Common Oral Pathogens
Csaba Dudás, Zsuzsanna Bardocz-Veres, Anita Iulia Gyulai, Silvia Izabella Pop, Melinda Székely, Bernadette Kerekes-Máthé, Mónika Kovács
Dentistry Journal.2024; 13(1): 17. CrossRef - Periradicular repair after single- and two-visit root canal treatments using ultrasonic irrigant activation and calcium hydroxide dressing of teeth with apical periodontitis: study protocol for randomized controlled trials
Gustavo M. Almeida, Vitor Hugo M. Carvalho, Érika B. P. Silva, Marco Antonio F. Cançado, Leonardo S. Barroso, Erica L. Queiroz, Tien Li An, Ana Paula D. Ribeiro, Jacy R. Carvalho-Junior, André F. Leite
Trials.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - In Vitro Evaluation of the Antibacterial Activity of EndoSeal MTA, iRoot SP, and AH Plus against Planktonic Bacteria
Siew Thong Mak, Xin Fang Leong, In Meei Tew, Endang Kumolosasi, Lishen Wong
Materials.2022; 15(6): 2012. CrossRef - Influence of apical preparation size and final irrigation protocol on the debridement of oval root canals
Carolina Pessoa Stringheta, Rina Andréa Pelegrine, Victor Angelo Martins Montalli, James L Gutmann, Carlos Eduardo da Silveira Bueno
Brazilian Dental Journal.2021; 32(6): 16. CrossRef
- Unveiling the correlation between in vivo endodontic reciprocate instrumentation and crack formation
- 2,558 View
- 29 Download
- 8 Crossref


 KACD
KACD

 First
First Prev
Prev


