Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
-
Apical root canal cleaning after preparation with endodontic instruments: a randomized trial
in vivo analysis - Volmir João Fornari, Mateus Silveira Martins Hartmann, José Roberto Vanni, Rubens Rodriguez, Marina Canali Langaro, Lauter Eston Pelepenko, Alexandre Augusto Zaia
- Restor Dent Endod 2020;45(3):e38. Published online June 24, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2020.45.e38
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
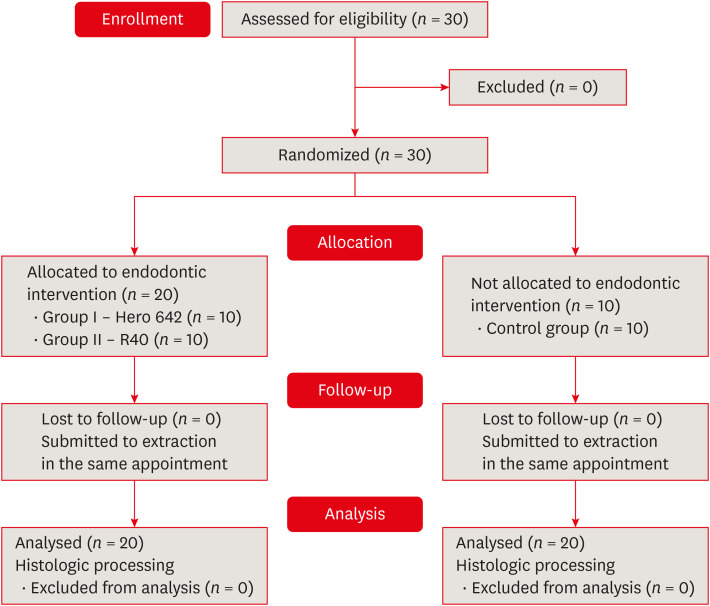
ePub Objectives This study aimed to evaluate vital pulp tissue removal from different endodontic instrumentation systems from root canal apical third
in vivo .Materials and Methods Thirty mandibular molars were selected and randomly divided into 2 test groups and one control group. Inclusion criteria were a positive response to cold sensibility test, curvature angle between 10 and 20 degrees, and curvature radius lower than 10 mm. Root canals prepared with Hero 642 system (size 45/0.02) (
n = 10) and Reciproc R40 (size 40/0.06) (n = 10) and control (n = 10) without instrumentation. Canals were irrigated only with saline solution during root canal preparation. The apical third was evaluated considering the touched/untouched perimeter and area to evaluate the efficacy of root canal wall debridement. Statistical analysis usedt -test for comparisons.Results Untouched root canal at cross-section perimeter, the Hero 642 system showed 41.44% ± 5.62% and Reciproc R40 58.67% ± 12.39% without contact with instruments. Regarding the untouched area, Hero 642 system showed 22.78% ± 6.42% and Reciproc R40 34.35% ± 8.52%. Neither instrument achieved complete cross-sectional root canal debridement. Hero 642 system rotary taper 0.02 instruments achieved significant greater wall contact perimeter and area compared to reciprocate the Reciproc R40 taper 0.06 instrument.
Conclusions Hero 642 achieved higher wall contact perimeter and area but, regardless of instrument size and taper, vital pulp during
in vivo instrumentation is not entirely removed.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Unveiling the correlation between in vivo endodontic reciprocate instrumentation and crack formation
Mateus Silveira Martins Hartmann, José Roberto Vanni, Karla Rovaris, Lucas Jeziorski Hartmann, Lauter Eston Pelepenko, Adriana de-Jesus-Soares, Volmir João Fornari
Journal of Dentistry.2024; 150: 105367. CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of stress distribution against the root canal wall at three different levels using novel NiTi rotary files – A finite element analysis
Rimjhim Singh, Sandeep Dubey, Palak Singh, Praveen Singh Samant, Suparna Ganguly Saha
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2024; 27(1): 62. CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of Ultrasonic and Sonic Irrigant Activation Systems: Assessing Extrusion Risk, Debridement, and Biofilm Removal in Distinct Apical Preparation Sizes
Sara Paixão, Pedro Sousa Gomes, Maria Helena Fernandes, Cláudia Rodrigues, Liliana Grenho
Applied Sciences.2024; 14(9): 3904. CrossRef - A Short Report on the Effectiveness of Edge Taper Platinum and XP-3D Shaper for the Reduction of Enterococcus faecalis Count in the Root Canal System: An Ex Vivo Study
Hanie Moaveni, Parastou Ghahari, Samira Behrad, Majid Mirmohammadkhani, Sobhan Rashmee, Somayeh Teimoori
Avicenna Journal of Dental Research.2024; 16(2): 77. CrossRef - Comparative in Vitro Study on the Antimicrobial Efficacy of Endodontic Sealers Against Common Oral Pathogens
Csaba Dudás, Zsuzsanna Bardocz-Veres, Anita Iulia Gyulai, Silvia Izabella Pop, Melinda Székely, Bernadette Kerekes-Máthé, Mónika Kovács
Dentistry Journal.2024; 13(1): 17. CrossRef - Periradicular repair after single- and two-visit root canal treatments using ultrasonic irrigant activation and calcium hydroxide dressing of teeth with apical periodontitis: study protocol for randomized controlled trials
Gustavo M. Almeida, Vitor Hugo M. Carvalho, Érika B. P. Silva, Marco Antonio F. Cançado, Leonardo S. Barroso, Erica L. Queiroz, Tien Li An, Ana Paula D. Ribeiro, Jacy R. Carvalho-Junior, André F. Leite
Trials.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - In Vitro Evaluation of the Antibacterial Activity of EndoSeal MTA, iRoot SP, and AH Plus against Planktonic Bacteria
Siew Thong Mak, Xin Fang Leong, In Meei Tew, Endang Kumolosasi, Lishen Wong
Materials.2022; 15(6): 2012. CrossRef - Influence of apical preparation size and final irrigation protocol on the debridement of oval root canals
Carolina Pessoa Stringheta, Rina Andréa Pelegrine, Victor Angelo Martins Montalli, James L Gutmann, Carlos Eduardo da Silveira Bueno
Brazilian Dental Journal.2021; 32(6): 16. CrossRef
- Unveiling the correlation between in vivo endodontic reciprocate instrumentation and crack formation
- 2,601 View
- 29 Download
- 8 Crossref

- Accidental injury of the inferior alveolar nerve due to the extrusion of calcium hydroxide in endodontic treatment: a case report
- Yooseok Shin, Byoung-Duck Roh, Yemi Kim, Taehyeon Kim, Hyungjun Kim
- Restor Dent Endod 2016;41(1):63-67. Published online January 6, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2016.41.1.63

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub During clinical endodontic treatment, we often find radiopaque filling material beyond the root apex. Accidental extrusion of calcium hydroxide could cause the injury of inferior alveolar nerve, such as paresthesia or continuous inflammatory response. This case report presents the extrusion of calcium hydroxide and treatment procedures including surgical intervention. A 48 yr old female patient experienced Calcipex II extrusion in to the inferior alveolar canal on left mandibular area during endodontic treatment. After completion of endodontic treatment on left mandibular first molar, surgical intervention was planned under general anesthesia. After cortical bone osteotomy and debridement, neuroma resection and neurorrhaphy was performed, and prognosis was observed. But no improvement in sensory nerve was seen following surgical intervention after 20 mon. A clinician should be aware of extrusion of intracanal medicaments and the possibility of damage on inferior alveolar canal. Injectable type of calcium hydroxide should be applied with care for preventing nerve injury. The alternative delivery method such as lentulo spiral was suggested on the posterior mandibular molar.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Nicolau syndrome in endodontics: A narrative review on calcium hydroxide extrusion and its therapeutic risks
Manisha Chaudhary, Akash Kumar Giri, Ashok Ayer
Saudi Endodontic Journal.2026; 16(1): 12. CrossRef - Invasion of Calcium Hydroxide Preparations Leading to Severe Chemical Nerve Injury Treated Through Nerve Repair Using Artificial Nerve Conduit: A Case Report
Akihiro Nishiyama, Andreas Neff, Takahiro Nakada, Takaharu Ariizumi, Akira Iwasaki, Keisuke Sugahara, Akira Katakura, Hannah Wesley
Case Reports in Dentistry.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Automatic localization of inferior alveolar nerve canal in panoramic dental images
Uma Maheswari Pandyan, Banumathi Arumugam, Ulaganathan Gurunathan, Shahul Hameed Kopuli Ashkar Ali
Signal, Image and Video Processing.2022; 16(5): 1389. CrossRef - Inferior alveolar nerve injury due to the extrusion of calcium hydroxide during endodontic treatment: A case report
Metin Berk Kasapoğlu, Gülce Ecem Doğancalı
Australian Endodontic Journal.2022; 48(2): 342. CrossRef - Inferior alveolar nerve canal segmentation by local features based neural network model
P. Uma Maheswari, A. Banumathi, G. Ulaganathan, R. Yoganandha
IET Image Processing.2022; 16(3): 703. CrossRef - Microsurgical Repair of Inferior Alveolar Nerve Injuries Associated With Endodontic Treatment: Results on Sensory Function and Relief of Pain
Keith A. Sonneveld, Kristopher L. Hasstedt, Roger A. Meyer, Shahrokh C. Bagheri
Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery.2021; 79(7): 1434. CrossRef - The significance of diagnosis and treatment planning in periapical lesion overfilled with calcium hydroxide paste
Kyoung-Hwa Jung, Eun-Young Kwon, Youn-Kyung Choi, So-Yeun Kim, Hye-Mi Jeon, Jeong-Kil Park
Journal of Dental Rehabilitation and Applied Science.2021; 37(2): 95. CrossRef - The anatomical relationship between the roots of erupted permanent teeth and the mandibular canal: a systematic review
Michał Puciło, Mariusz Lipski, Magdalena Sroczyk-Jaszczyńska, Aleksandra Puciło, Alicja Nowicka
Surgical and Radiologic Anatomy.2020; 42(5): 529. CrossRef - Massive extrusion of calcium hydroxide paste containing barium sulphate during endodontic treatment
Jéssica Montenegro Fonsêca, Natália Rangel Palmier, Gleyson Kleber Amaral‐Silva, Lady Paola Aristizabal Arboleda, José Flávio Affonso Almeida, Mario Fernando de Goes, Pablo Agustin Vargas, Marcio Ajudarte Lopes, Alan Roger Santos‐Silva
Australian Endodontic Journal.2020; 46(2): 257. CrossRef - The double-edged sword of calcium hydroxide in endodontics
Alan H. Gluskin, Gordon Lai, Christine I. Peters, Ove A. Peters
The Journal of the American Dental Association.2020; 151(5): 317. CrossRef - Endodontic-related inferior alveolar nerve injuries: A review and a therapeutic flow chart
R. Castro, M. Guivarc'h, J.M. Foletti, J.H. Catherine, C. Chossegros, L. Guyot
Journal of Stomatology, Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery.2018; 119(5): 412. CrossRef - Relationship between Root Apices and the Mandibular Canal: A Cone-beam Computed Tomographic Comparison of 3 Populations
Alex Lvovsky, Shir Bachrach, Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Ajinkya Pawar, Oleg Levinzon, Joe Ben Itzhak, Michael Solomonov
Journal of Endodontics.2018; 44(4): 555. CrossRef - A case of high density abnormality in x-ray findings of mandible caused by leakage of root canal filling paste
Haruko Kashiwamura, Kyoko Oka, Yoko Tuchihashi, Hanako Yoshioka, Mayumi Kato, Atsuko Baba, Toyohiro Kagawa, Kazuhiko Okamura, Masao Ozaki
Pediatric Dental Journal.2017; 27(3): 162. CrossRef - Oral dysesthesia
Christopher J. Spencer, Gary D. Klasser
The Journal of the American Dental Association.2017; 148(12): 941. CrossRef - Microsurgical Decompression of Inferior Alveolar Nerve After Endodontic Treatment Complications
Bernardo Bianchi, Andrea Ferri, Andrea Varazzani, Michela Bergonzani, Enrico Sesenna
Journal of Craniofacial Surgery.2017; 28(5): 1365. CrossRef
- Nicolau syndrome in endodontics: A narrative review on calcium hydroxide extrusion and its therapeutic risks
- 3,702 View
- 43 Download
- 15 Crossref

- Scanning electron microscopic study on the efficacy of root canal wall debridement of rotary Ni-Ti instruments with different cutting angle
- In-soo Jeon, Kee-yeon Kum, Seong-ho Park, Tai-cheol Yoon
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2002;27(6):577-586. Published online November 30, 2002
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2002.27.6.577
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purpose of this in vitro study was to compare the effects of root canal debridement following rotary Ni-Ti instruments with positive versus negative rake angle. Seventy sound, extracted human anterior teeth & premolars were randomly divided into four groups. The used rotary instruments were Ni-Ti HERO 642(Micro-Mega in France, 20 specimen), Ni-Ti ProFile(Maillefer, Ballaigues, Switzerland, 20 specimen), stainless steel engine reamer(Mani, Matsutani Seisakusho Co.,Japan, 20 specimen) and negative control group(10 specimen) was only extirpated with barbed broach(Mani, Matsutani Seisakusho Co.,Japan)
Group 1 & 2 teeth were prepared to a #40 at the apex followed by 1 mm using crown-down technique. Group 3 teeth were instrumented from a #15 to a #40 in sequential order. After preparation and final irrigation, the roots split longitudinally into a bucco-lingual direction. Root halves were cross-sectioned in apical third portion again. all root specimens were prepared for SEM investigation & photographed. Separate evaluations were undertaken for smear layer on prepared walls with a five score-index for each using reference photograph in root halves. the penetration depth of smear layer into dentinal tubules was also estimated in the other halves. the following results were obtained :
1. Smear layer was observed on all the prepared walls with three experimental groups except negative control group
2. Smear layer characteristics
1) HERO 642 groups showed snowy & dusty appearance & were observed only few some dentinal tubuli open on the prepared walls, and the penetration depth of it into dentinal tubules may be 1-2 µm thick.
2) ProFile groups showed shiny & burnished appearance & complete root canal wall covered by a homogenous smear layer with no open dentinal tubuli and penetration depth of it into dentinal tubules may be 1-2 µm thick.
3) Engine reamer groups showed obviously file's passed tracks on the prepared walls & were observed complete root canal wall covered by a homogenous smear layer with no open dentinal tubuli.
The results revealed that a completely clean root canal could not be achieved regardless of positive & negative rake angle, which is in accordance with the majority of studies on root canal cleanliness.
In conclusion, throughout irrigation with antibacterial solutions or chelating agents is recommended to remove the smear layer on prepared canal walls.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparative evaluation of dentin volume removal and centralization of the root canal after shaping with the ProTaper Universal, ProTaper Gold, and One-Curve instruments using micro-CT
Hatice Yalniz, Mehrdad Koohnavard, Aysenur Oncu, Berkan Celikten, Ayse Isil Orhan, Kaan Orhan
Journal of Dental Research, Dental Clinics, Dental Prospects.2021; 15(1): 47. CrossRef - Microorganism penetration in dentinal tubules of instrumented and retreated root canal walls.In vitroSEM study
Saad Al-Nazhan, Alaa Al-Sulaiman, Fellwa Al-Rasheed, Fatimah Alnajjar, Bander Al-Abdulwahab, Abdulhakeem Al-Badah
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2014; 39(4): 258. CrossRef - Shaping characteristics of two different motions nickel titanium file: a preliminary comparative study of surface profile and dentin chip
So-Ra Park, Se-Hee Park, Kyung-Mo Cho, Jin-Woo Kim
Journal of Dental Rehabilitation and Applied Science.2014; 30(2): 121. CrossRef
- Comparative evaluation of dentin volume removal and centralization of the root canal after shaping with the ProTaper Universal, ProTaper Gold, and One-Curve instruments using micro-CT
- 1,141 View
- 0 Download
- 3 Crossref


 KACD
KACD

 First
First Prev
Prev


